Diode
Use this image
Can I reuse this image without permission? Yes
Object images on the Ingenium Collection’s portal have the following Creative Commons license:
Copyright Ingenium / CC BY-NC-ND (Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)
ATTRIBUTE THIS IMAGE
Ingenium,
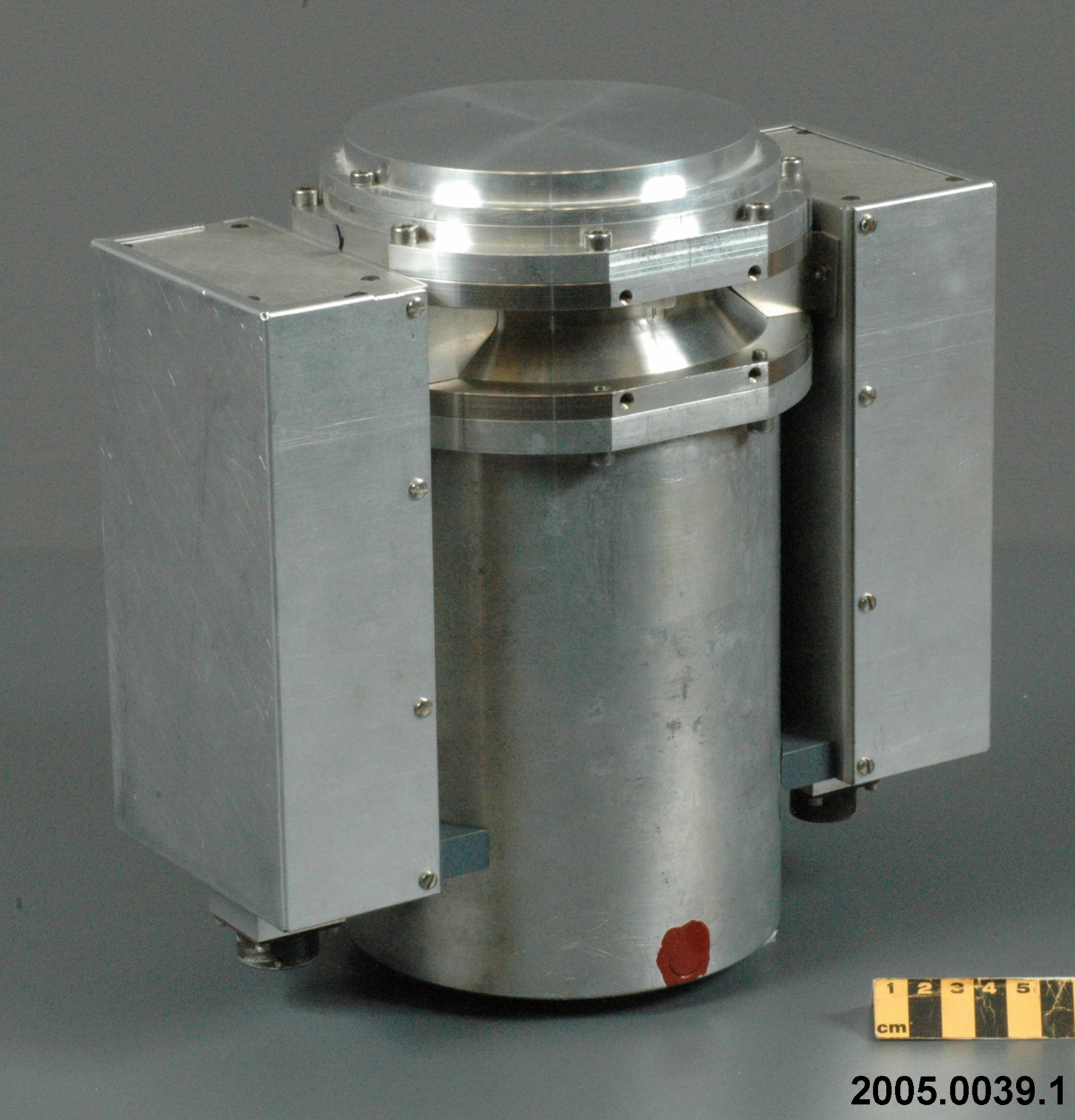
2005.0039.001
Permalink:
Ingenium is releasing this image under the Creative Commons licensing framework, and encourages downloading and reuse for non-commercial purposes. Please acknowledge Ingenium and cite the artifact number.
DOWNLOAD IMAGEPURCHASE THIS IMAGE
This image is free for non-commercial use.
For commercial use, please consult our Reproduction Fees and contact us to purchase the image.
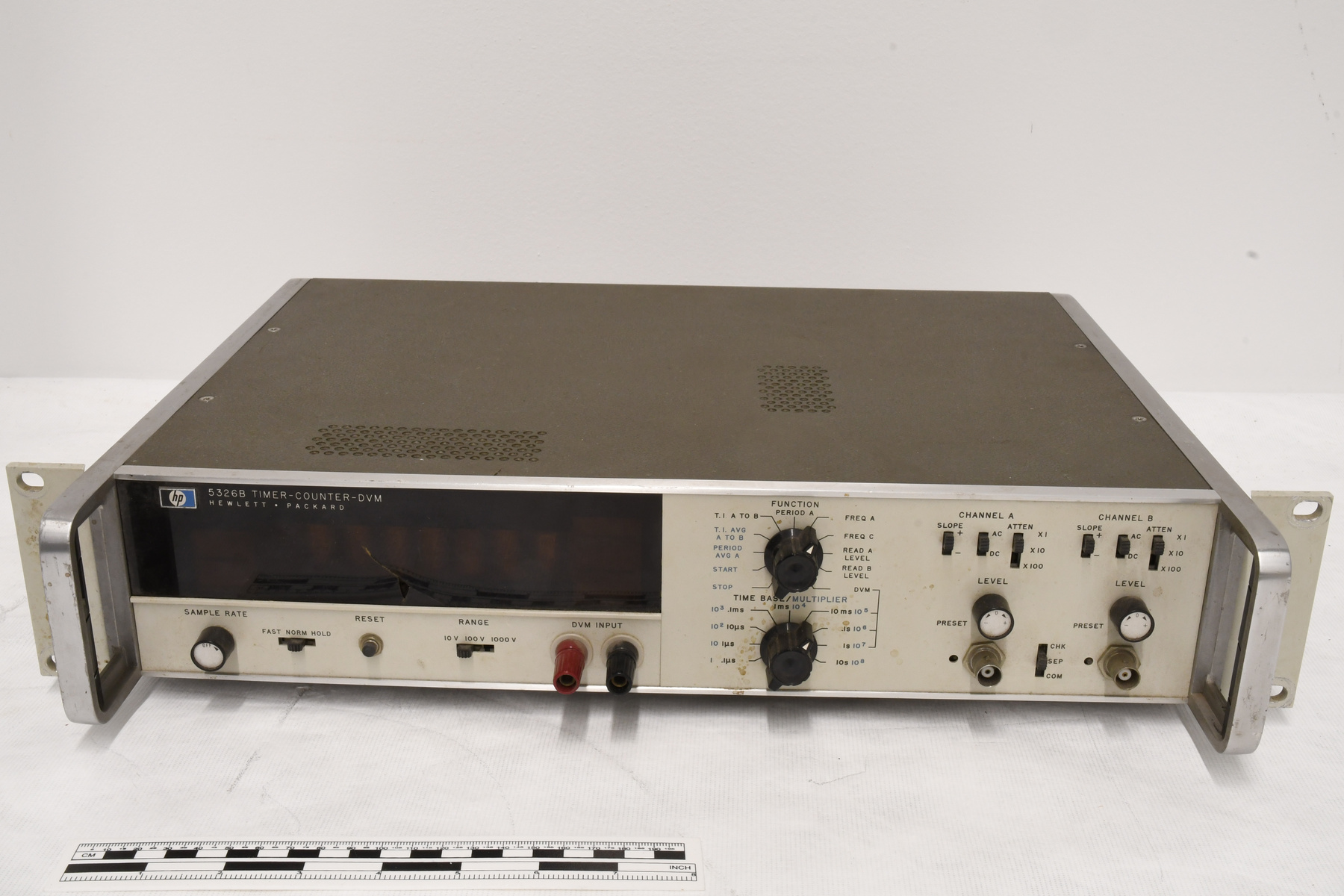
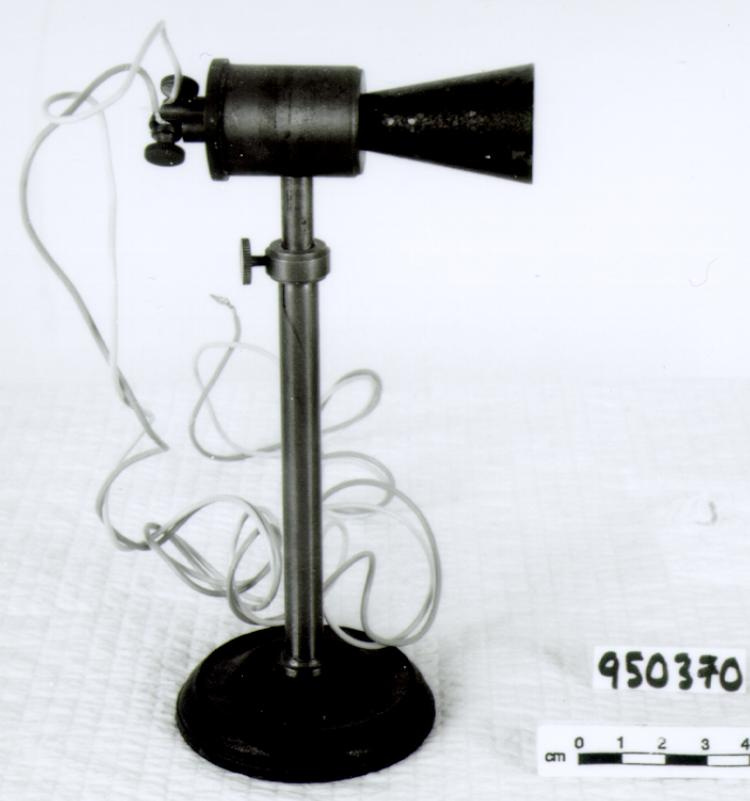
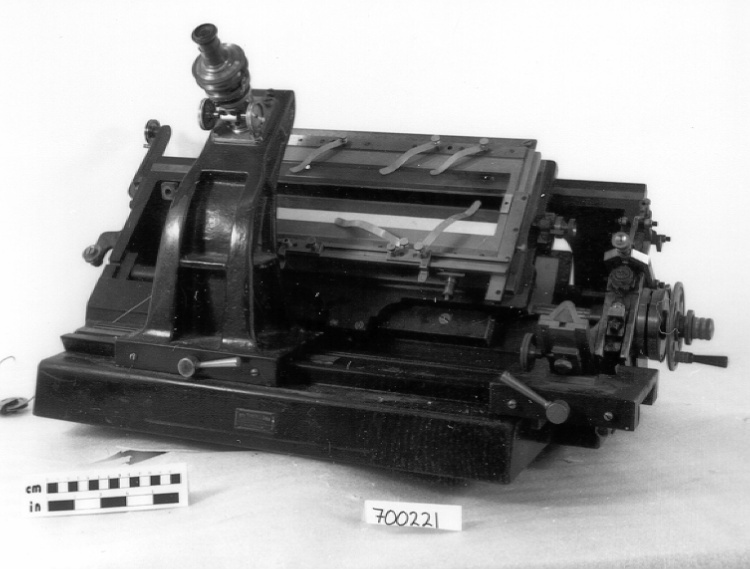
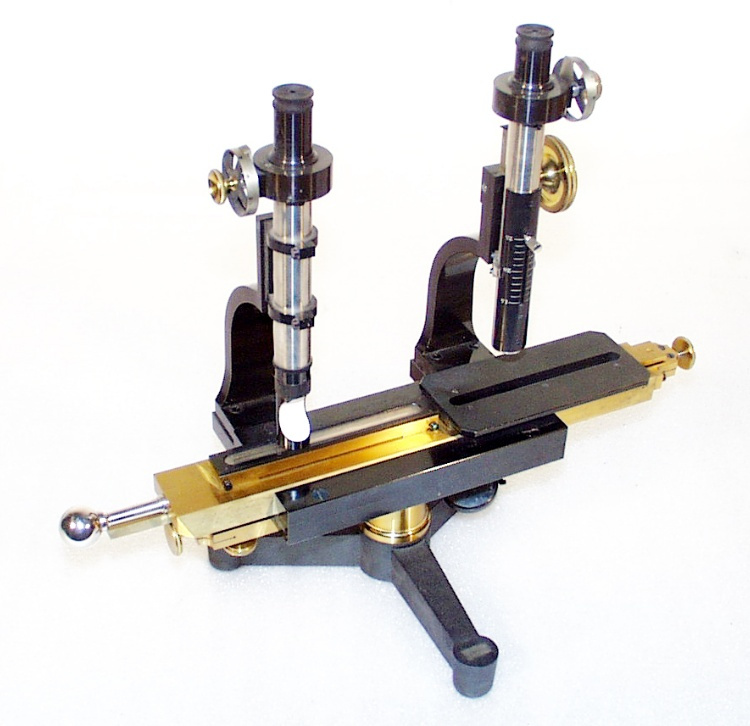
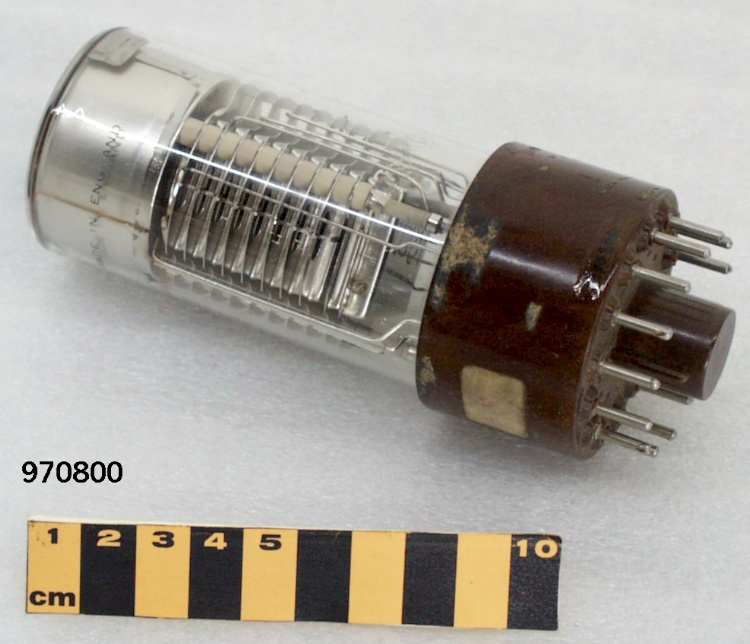
- OBJECT TYPE
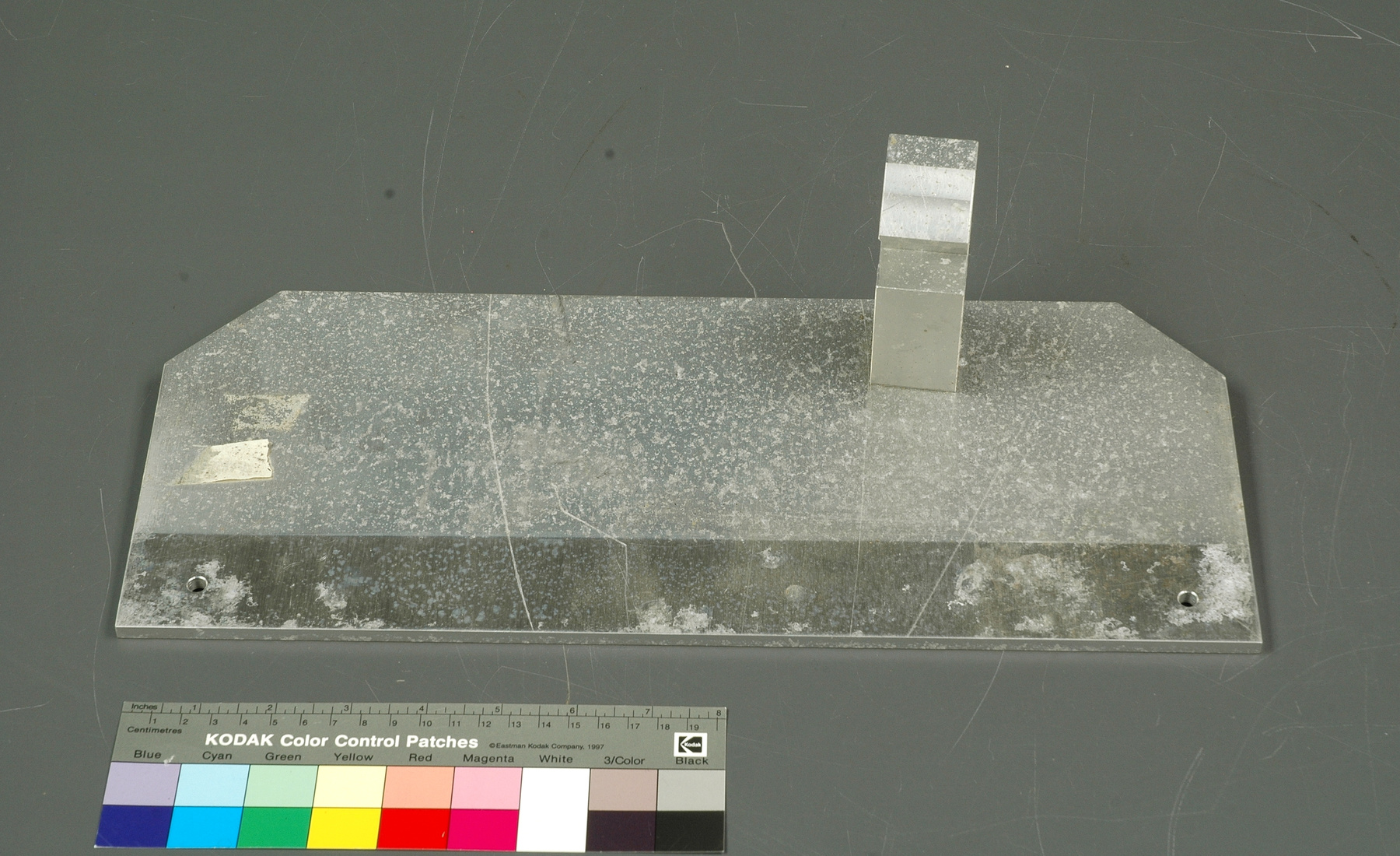
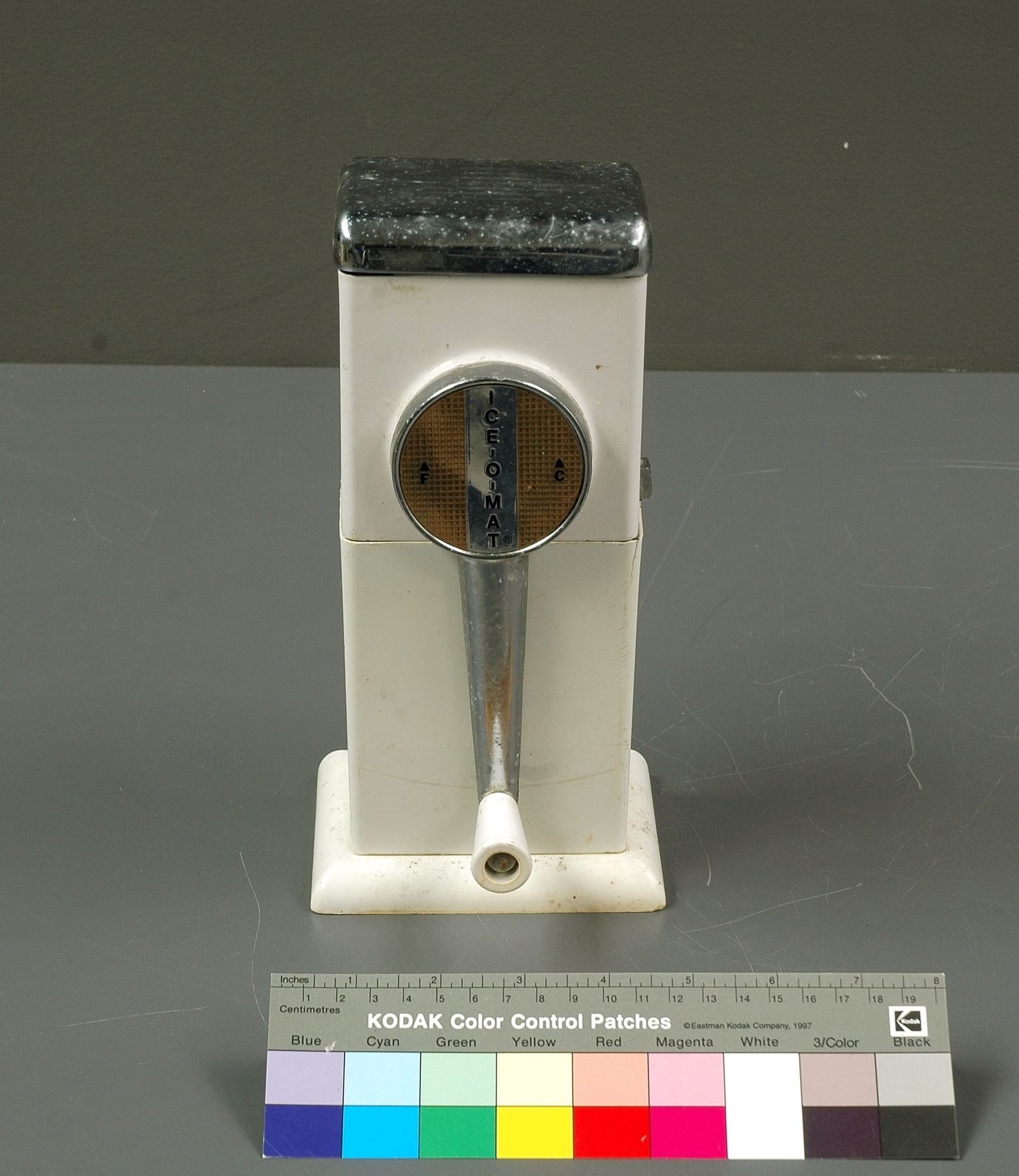
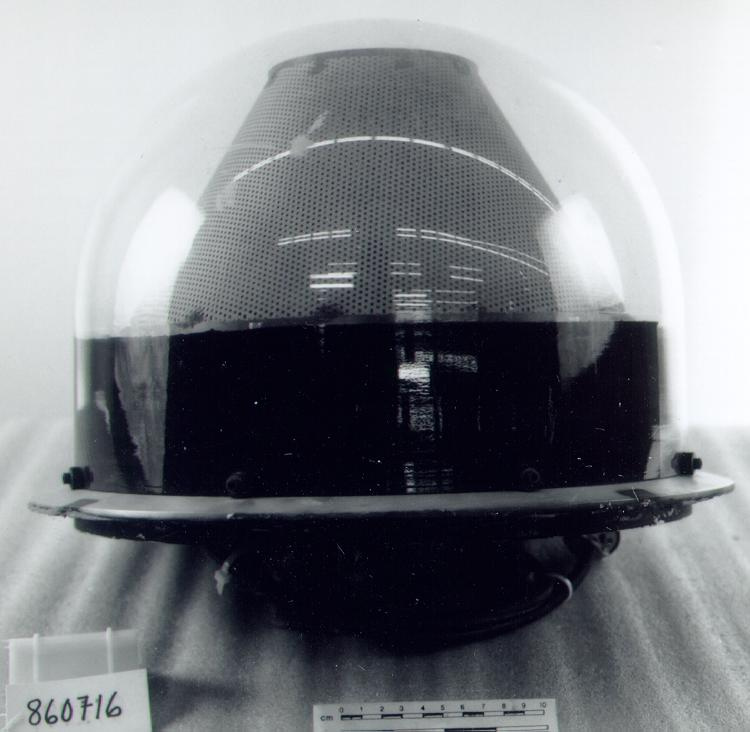
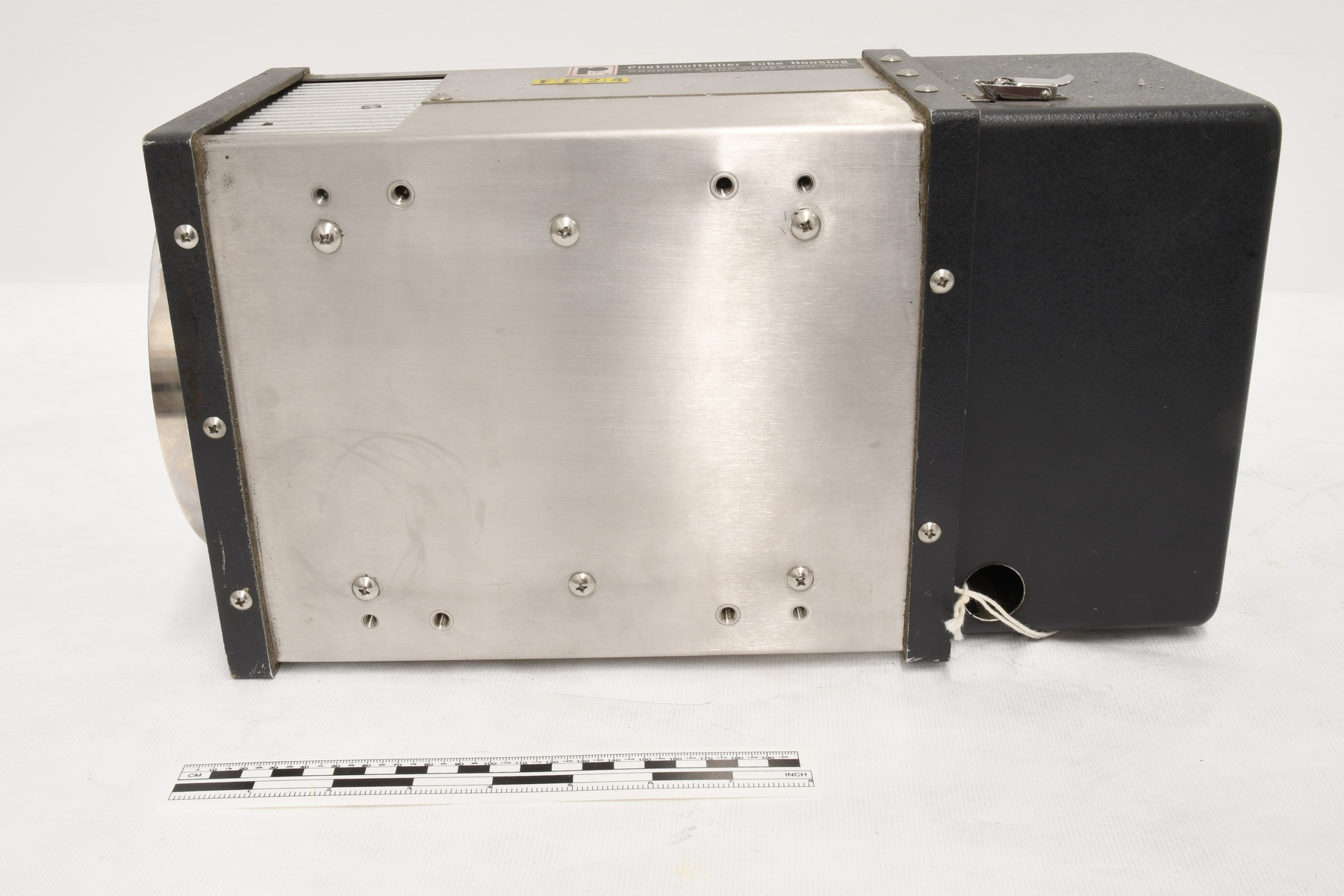
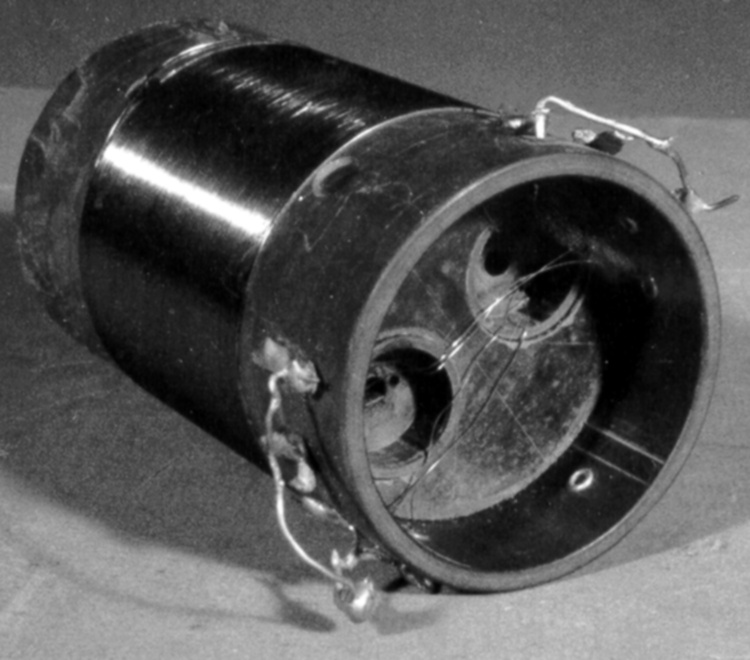
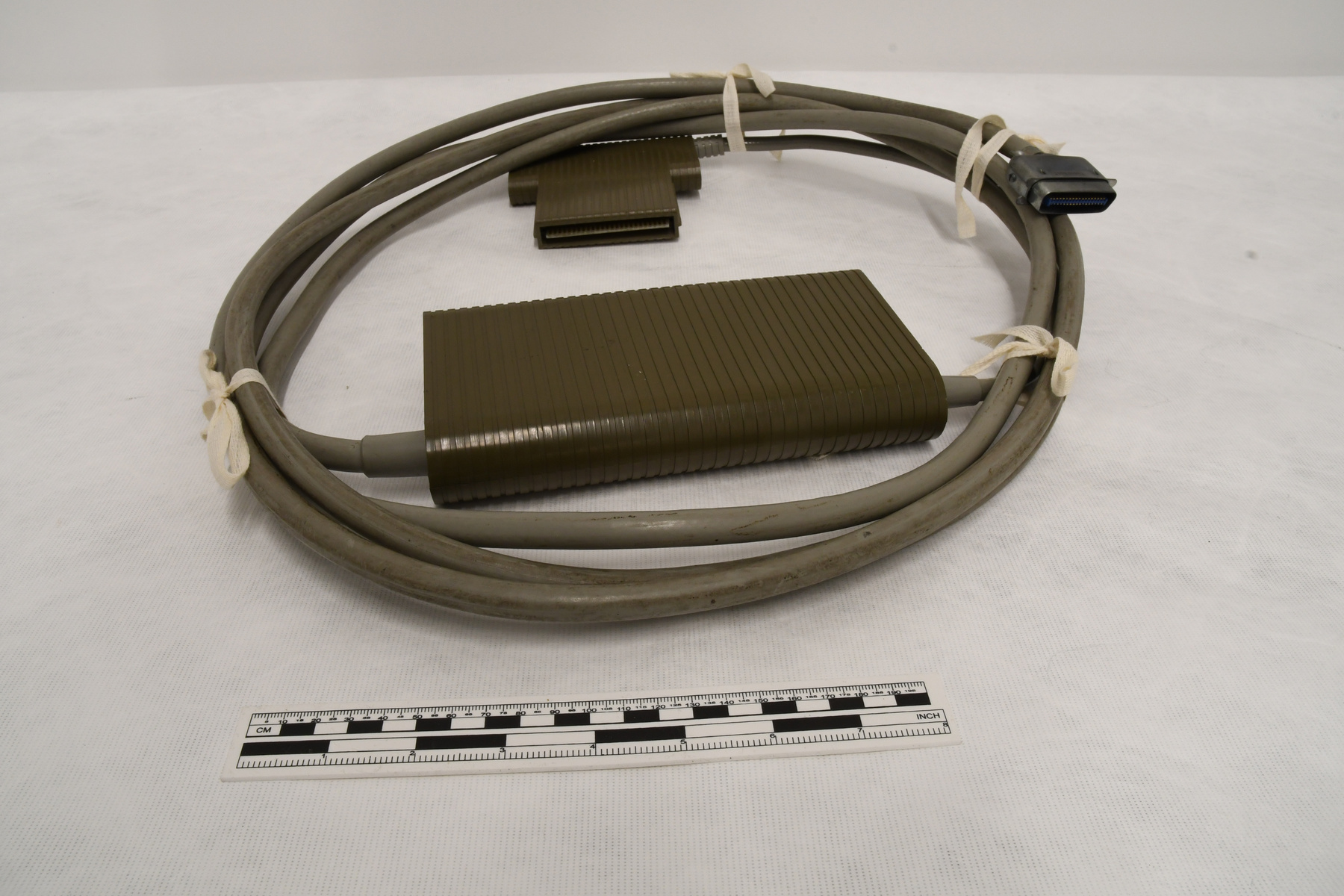
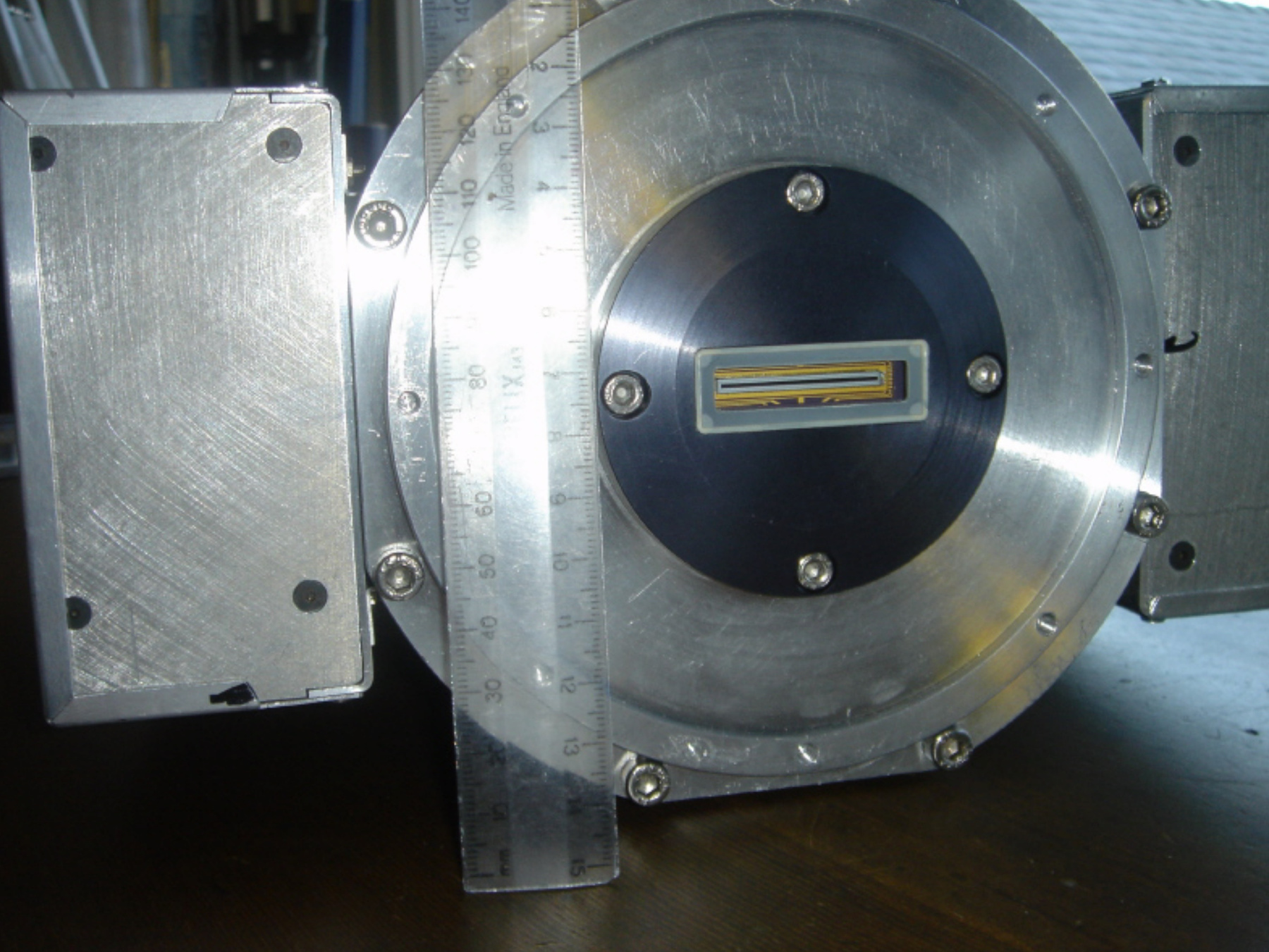
- Image/photodiode
- DATE
- 1975
- ARTIFACT NUMBER
- 2005.0039.001
- MANUFACTURER
- EG & G Inc.
- MODEL
- RL-1872F
- LOCATION
- Wellesley, Massachusetts, United States of America
More Information
General Information
- Serial #
- N/A
- Part Number
- 1
- Total Parts
- 1
- AKA
- Reticon
- Patents
- N/A
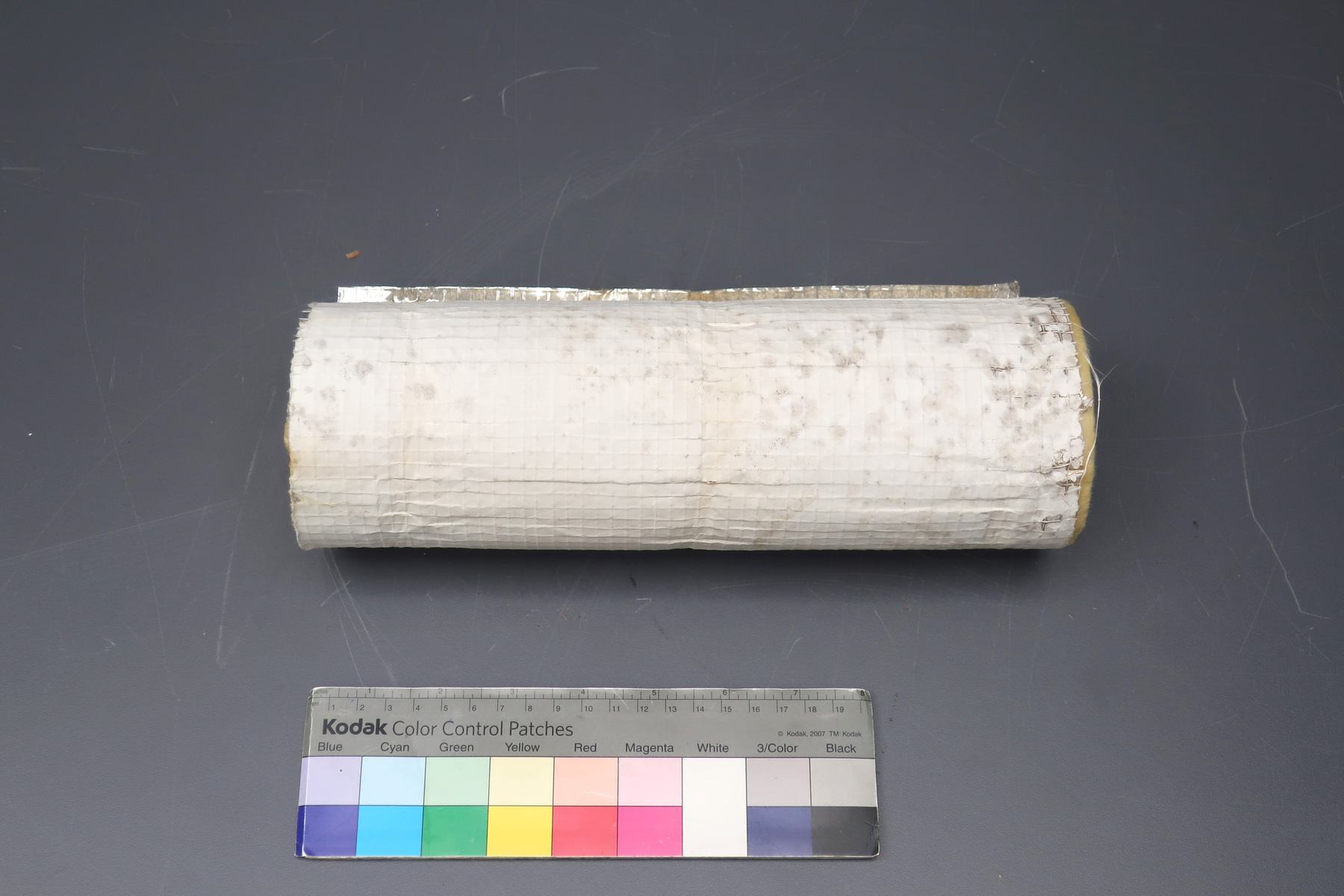
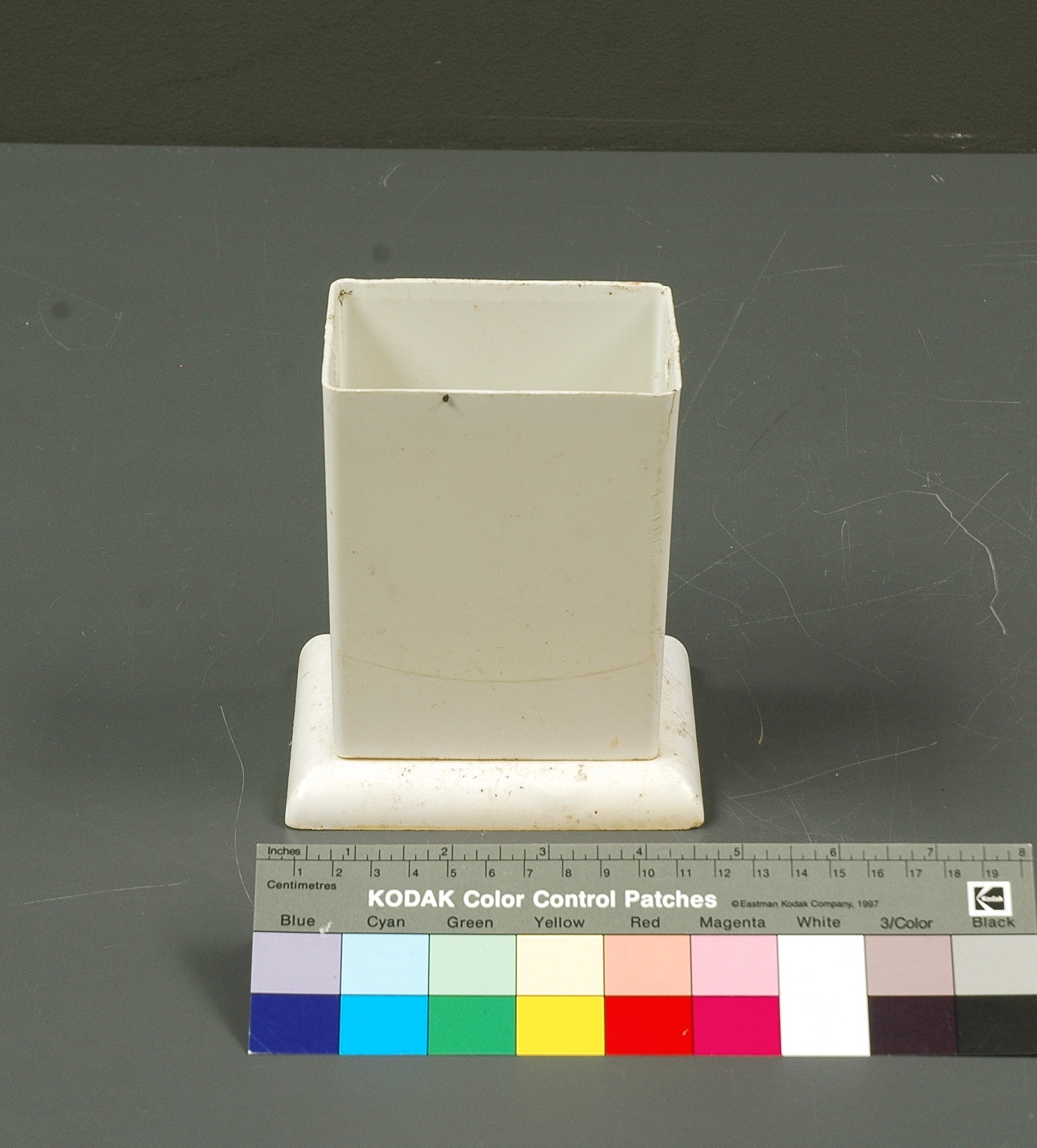
- General Description
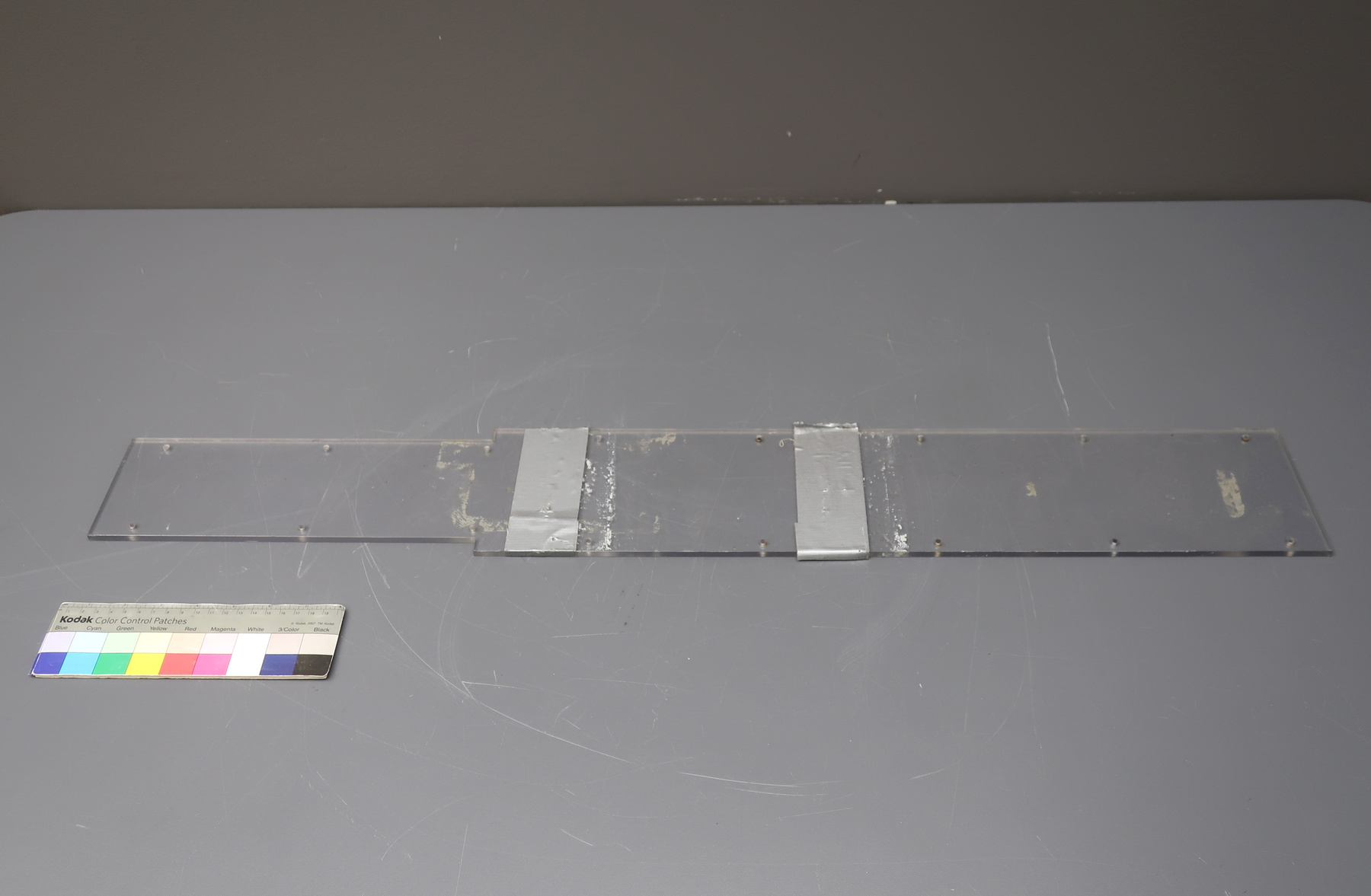
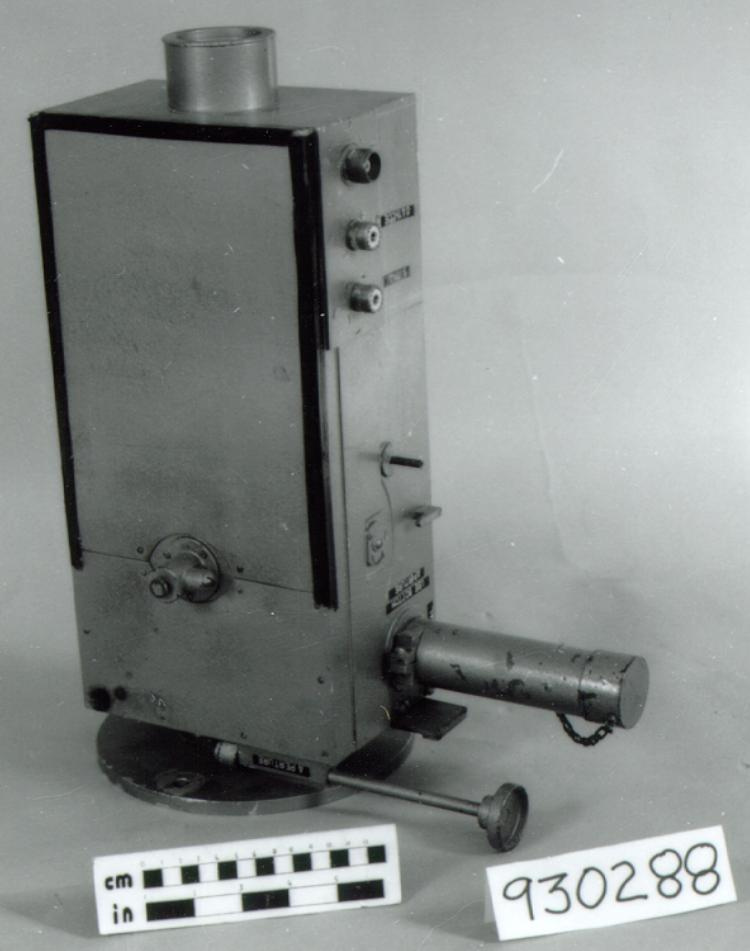
- aluminum casing/ metal parts/ synthetic parts
Dimensions
Note: These reflect the general size for storage and are not necessarily representative of the object's true dimensions.
- Length
- 26.2 cm
- Width
- 15.0 cm
- Height
- 26.5 cm
- Thickness
- N/A
- Weight
- N/A
- Diameter
- N/A
- Volume
- N/A
Lexicon
- Group
- Astronomy
- Category
- Research
- Sub-Category
- N/A
Manufacturer
- AKA
- EG&G
- Country
- United States of America
- State/Province
- Massachusetts
- City
- Wellesley
Context
- Country
- Canada
- State/Province
- British Columbia
- Period
- circa 1970+
- Canada
-
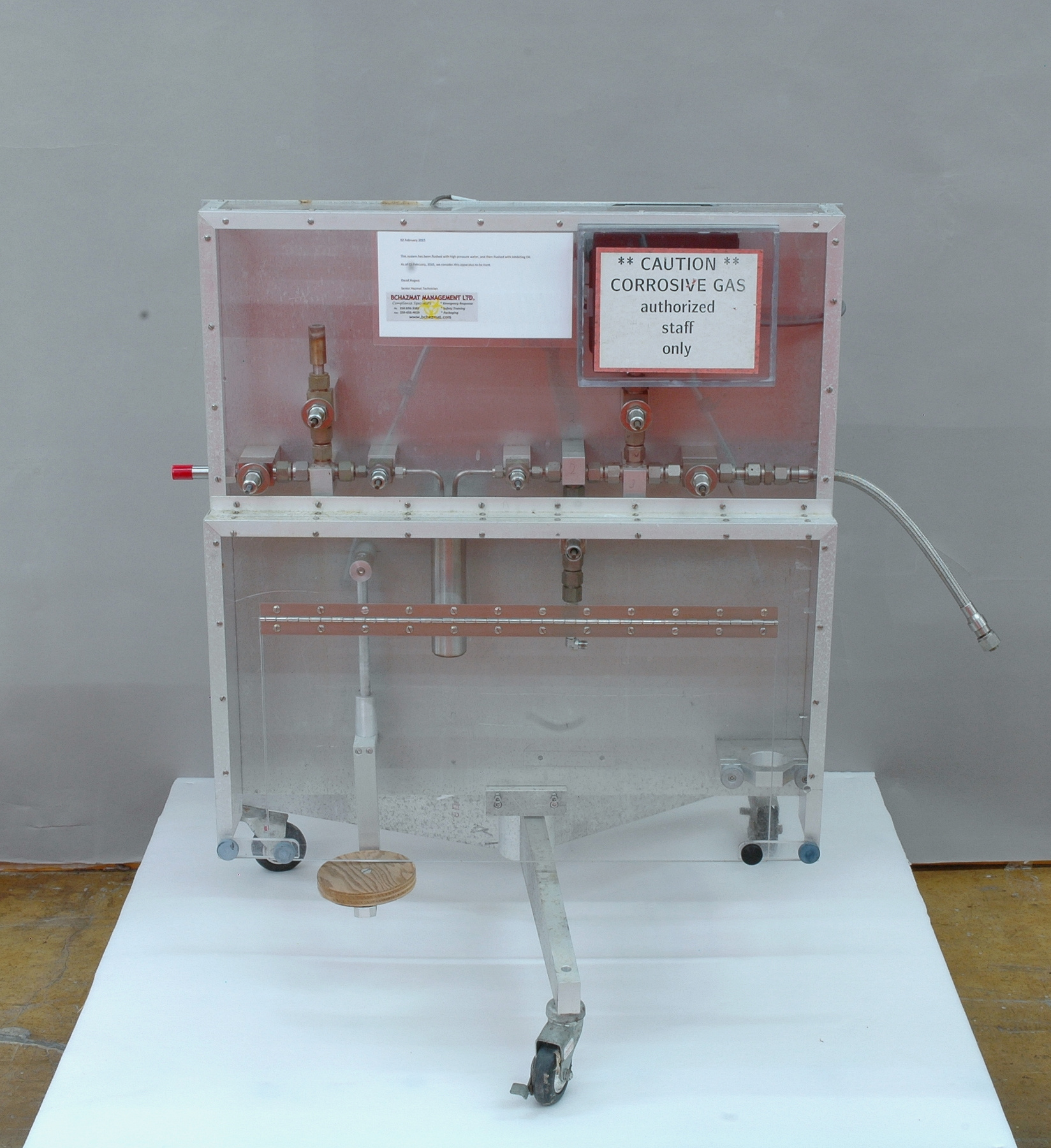
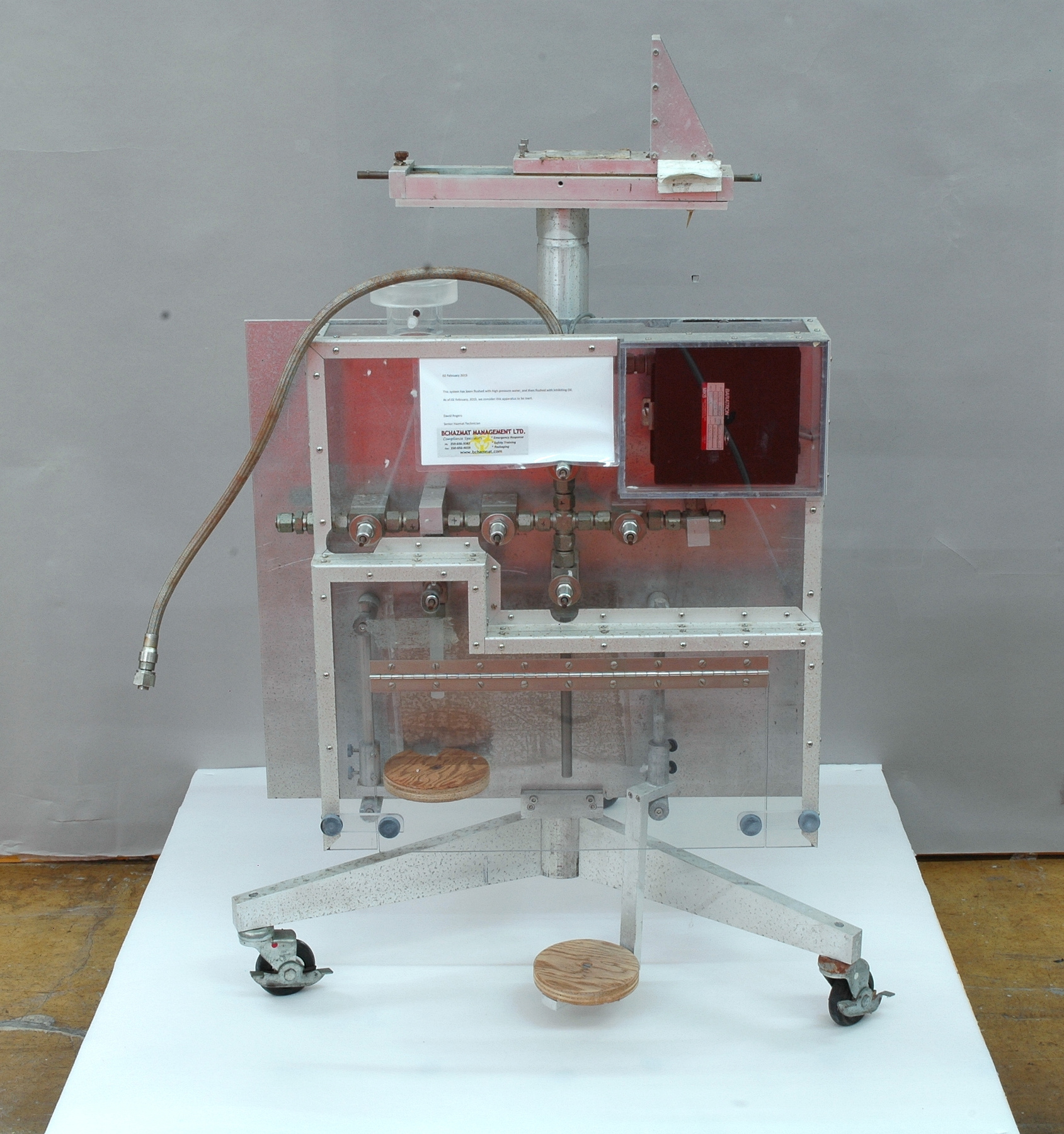
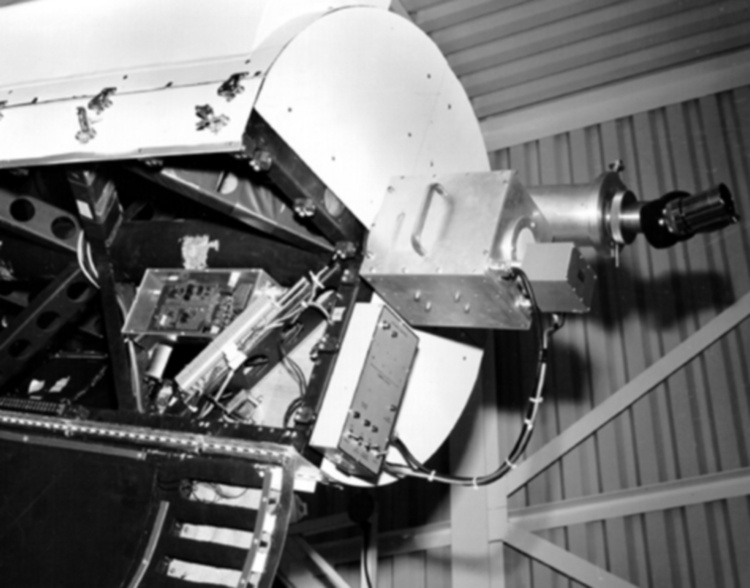
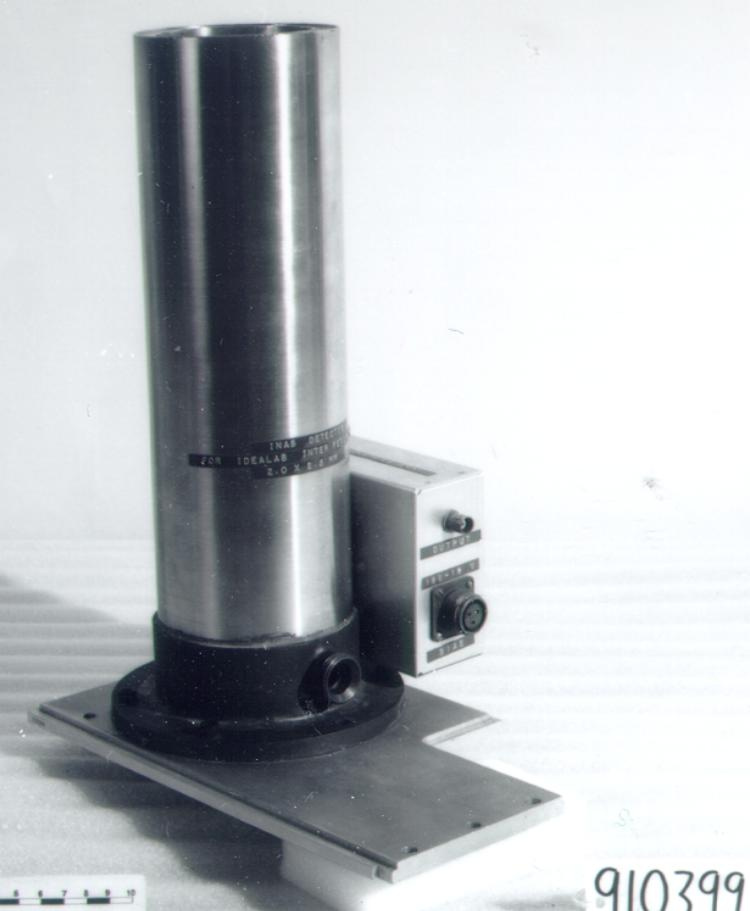
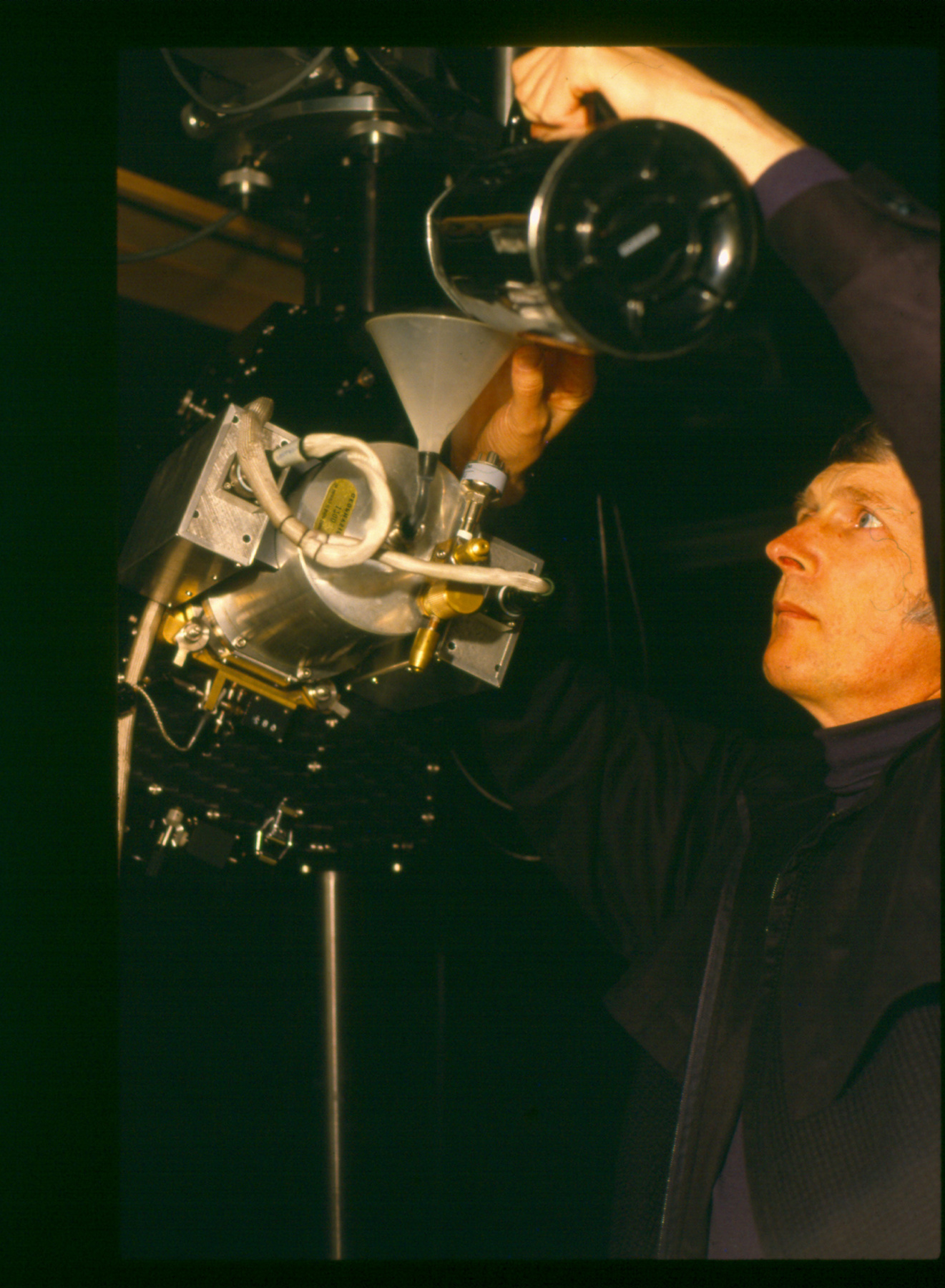
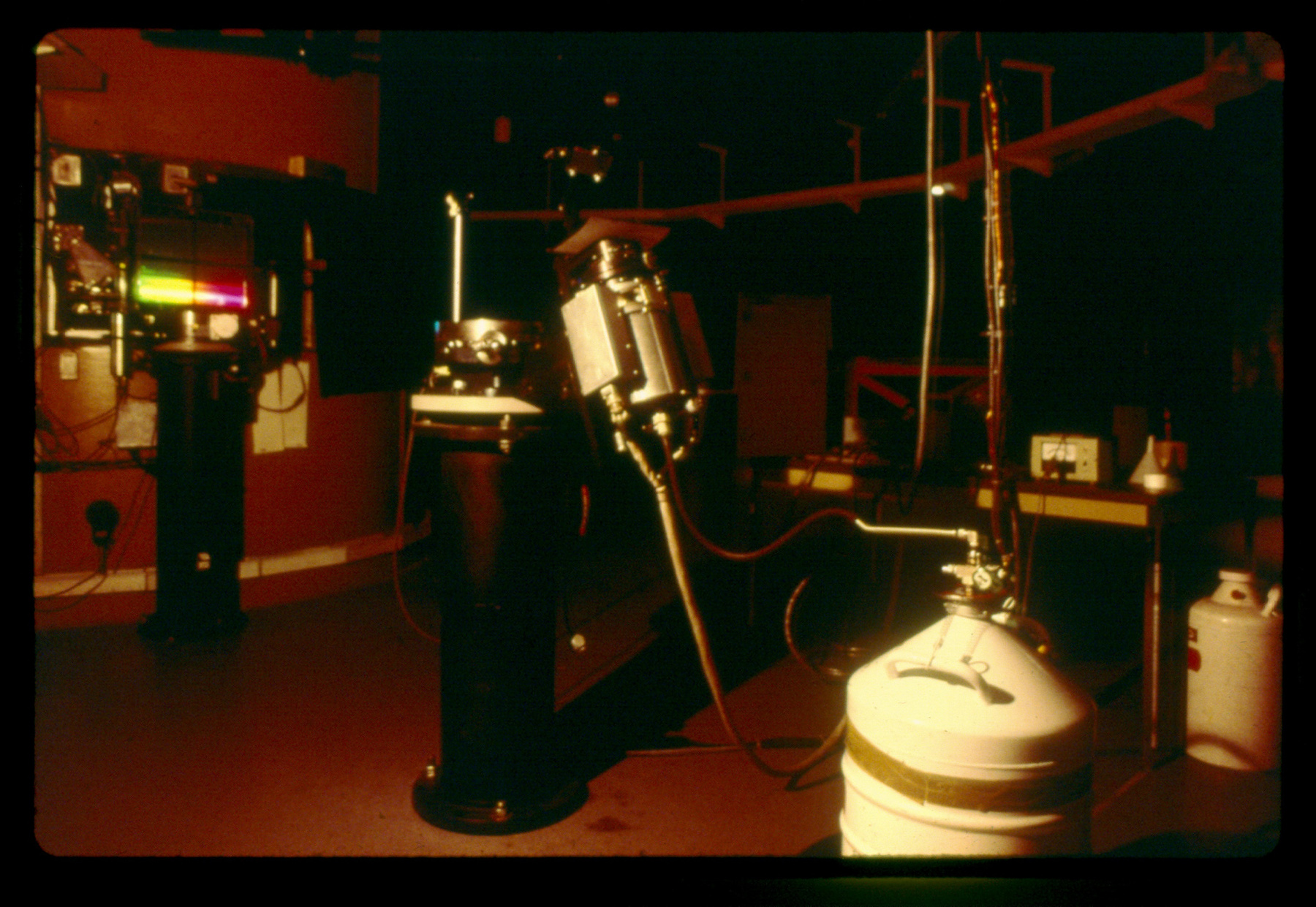
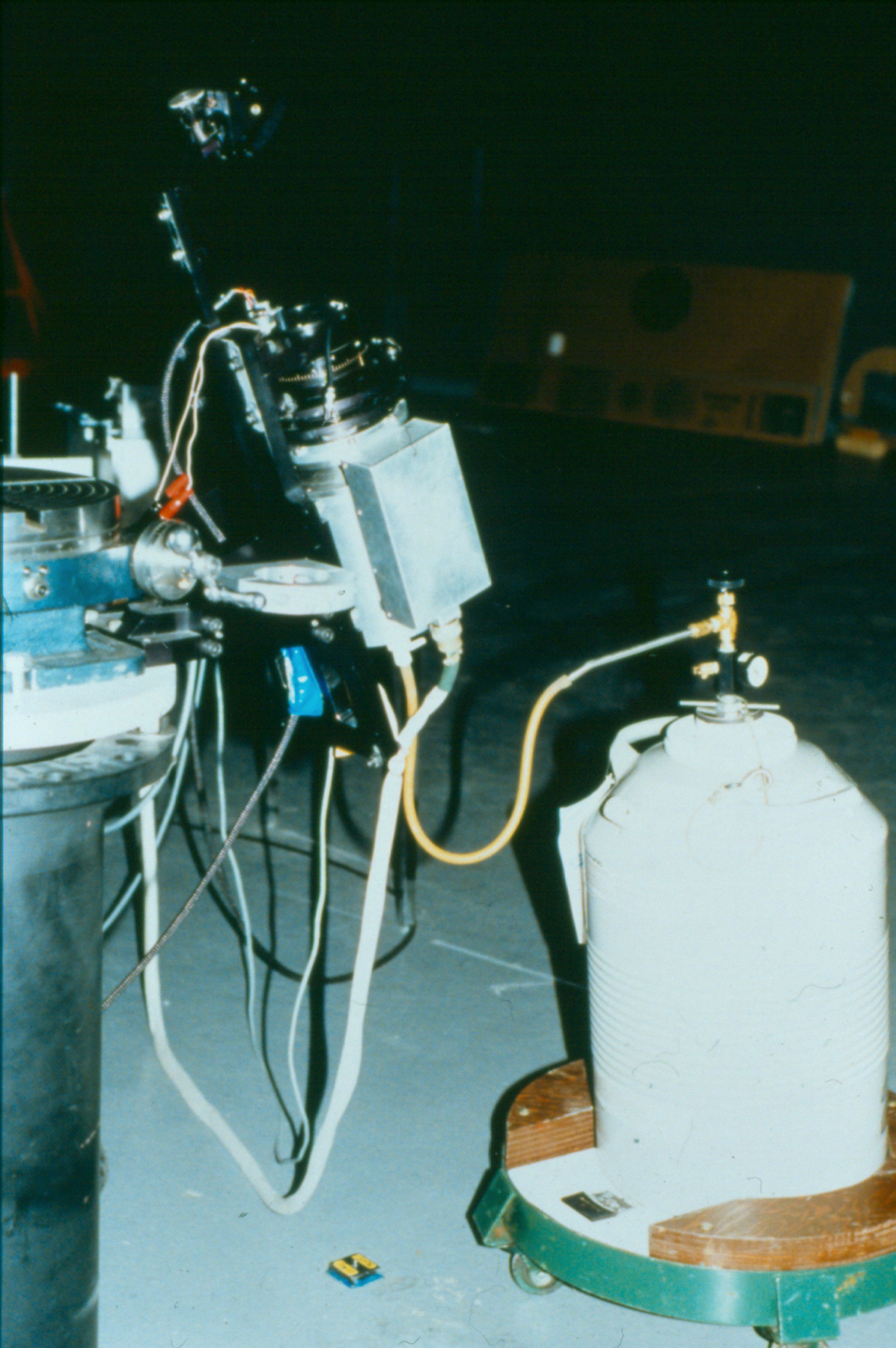
The reticon was a experimental device used by Canadian astronomer Gordon A.H. Walker in the 1970s to develop more sensitive detectors for astronomical observations. He was in the Dept. of Geophysics and Astronomy at the University of British Columbia and worked closely with staff (especially the tech staff during instrument development) at the Dominion Astrophysical Observatory in Victoria. Dr. Walker and his group at UBC were doing ground breaking research with these devices and they are (or almost) unique in Canada and rare world wide at least for astronomical use. Two or three groups were experimenting with similar technology in the US and UK. One of the major elements of Walker's research was to verify the accuracy of the systems compared to traditional techniques. - Function
-
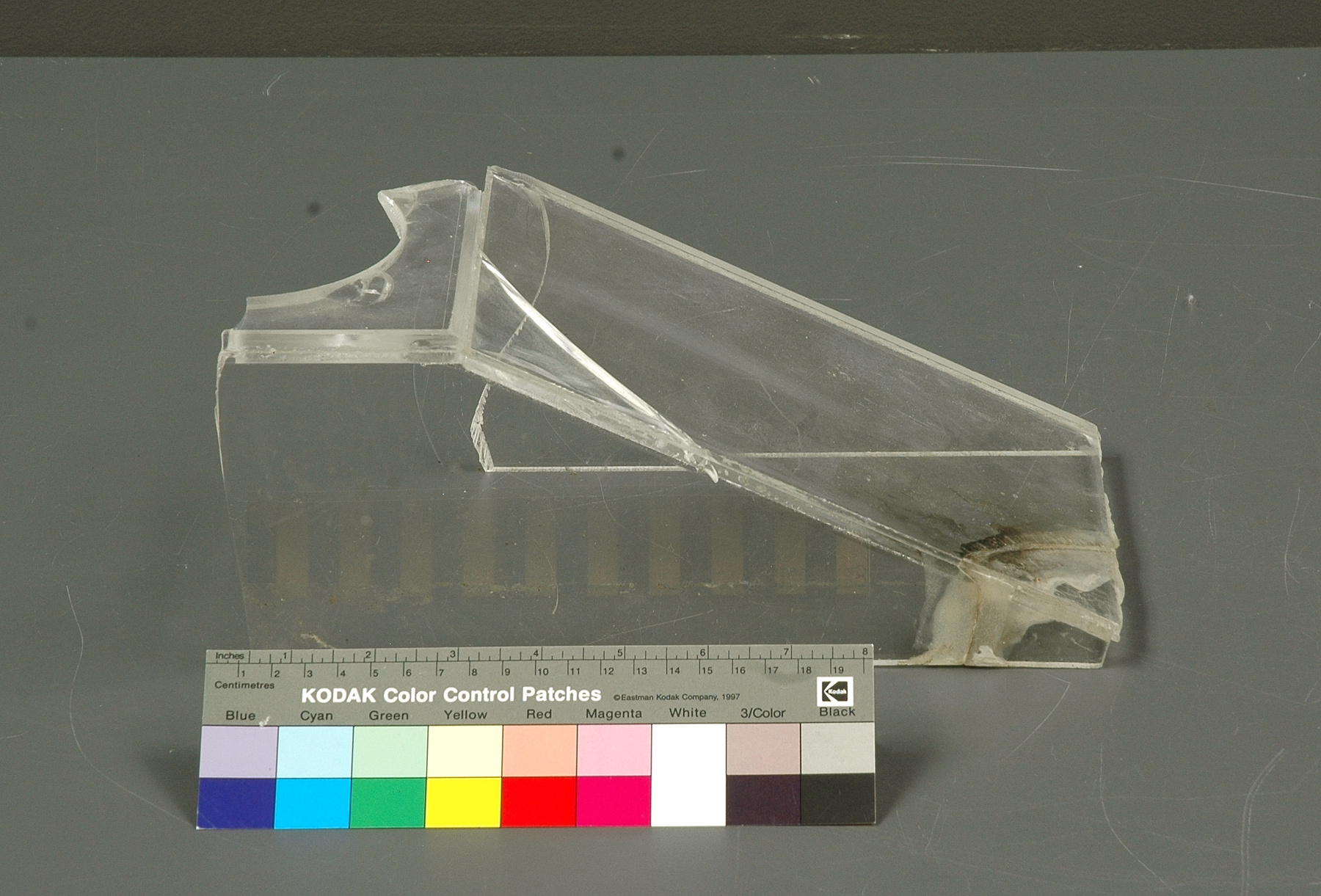
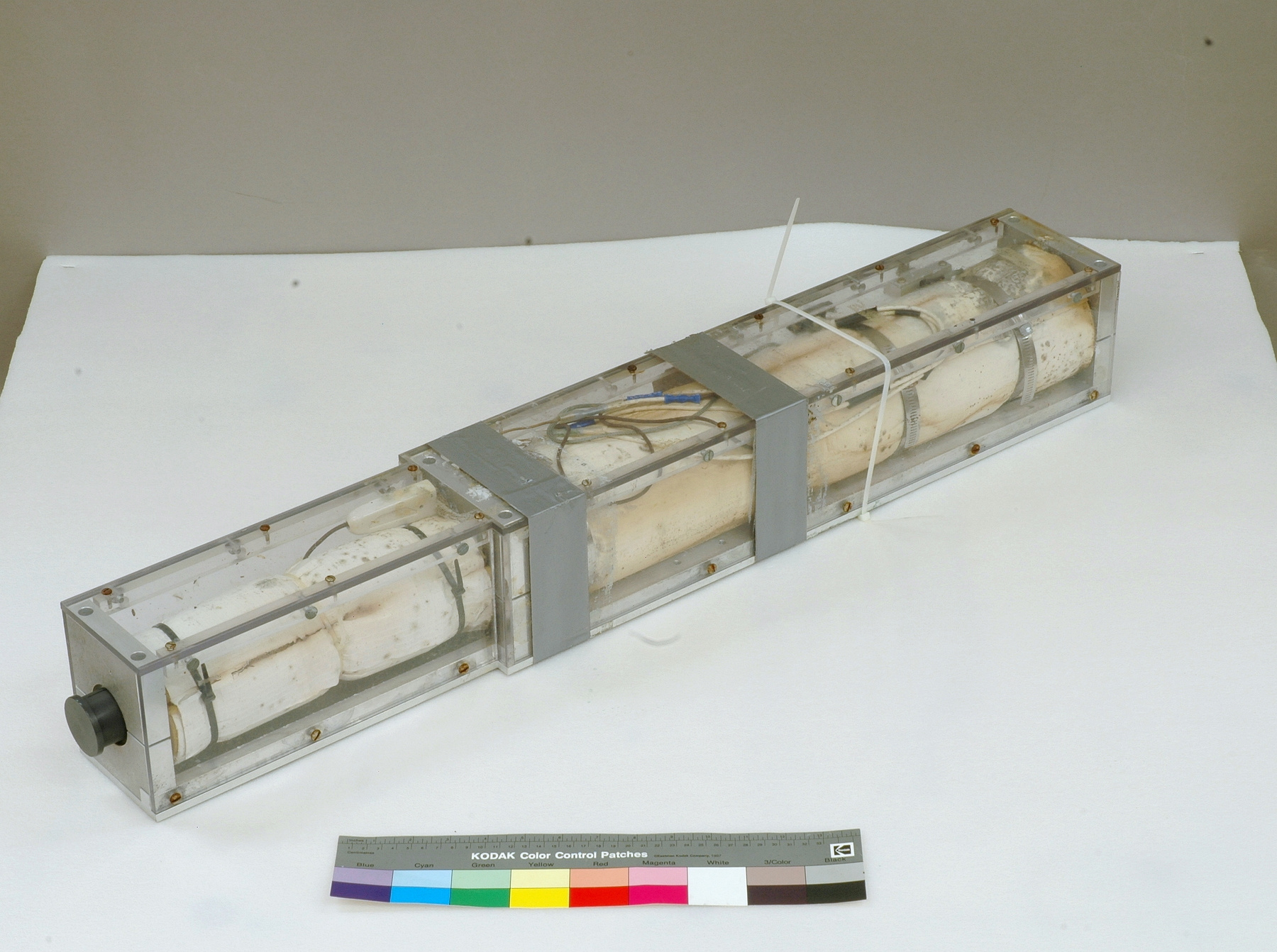
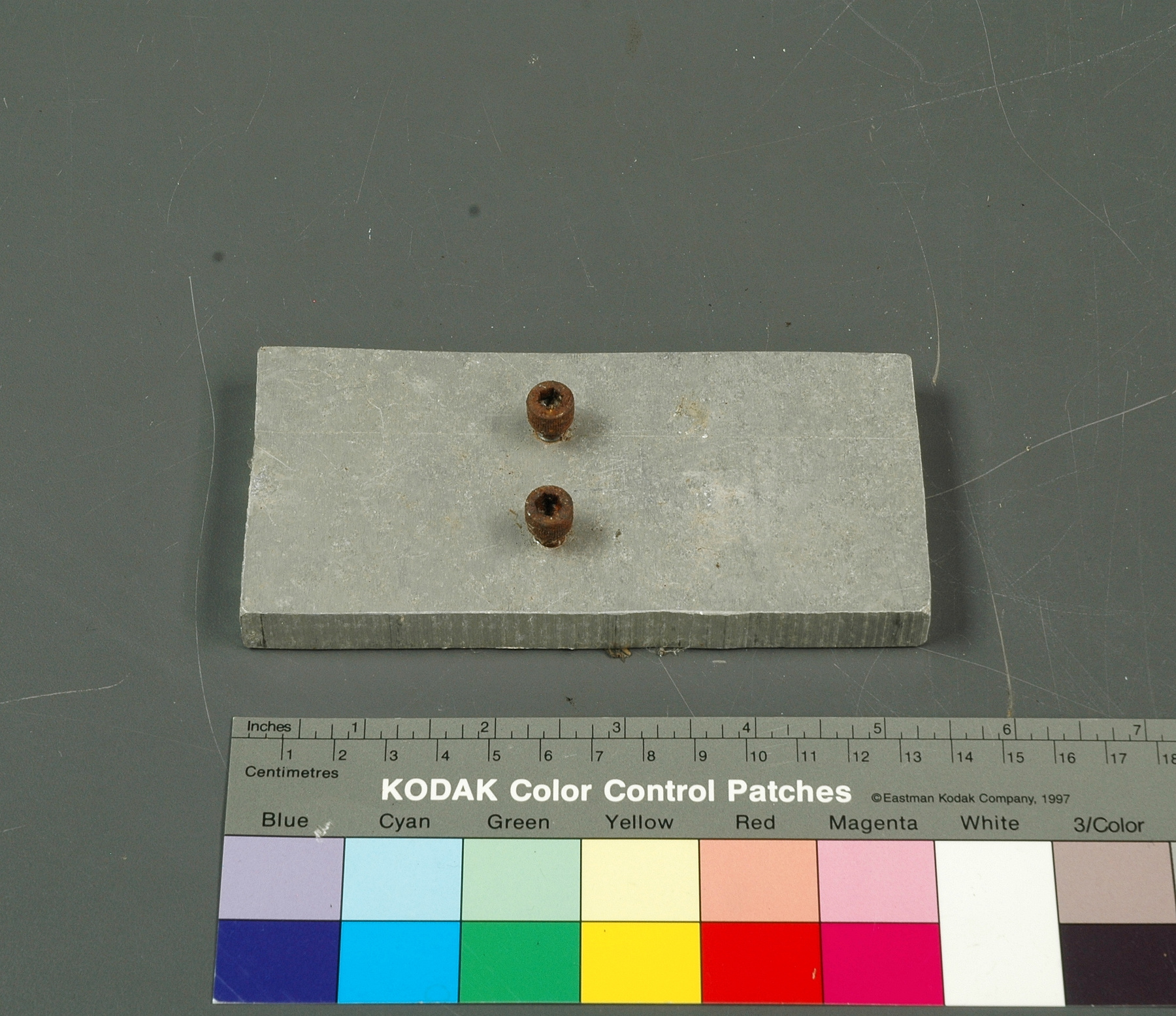
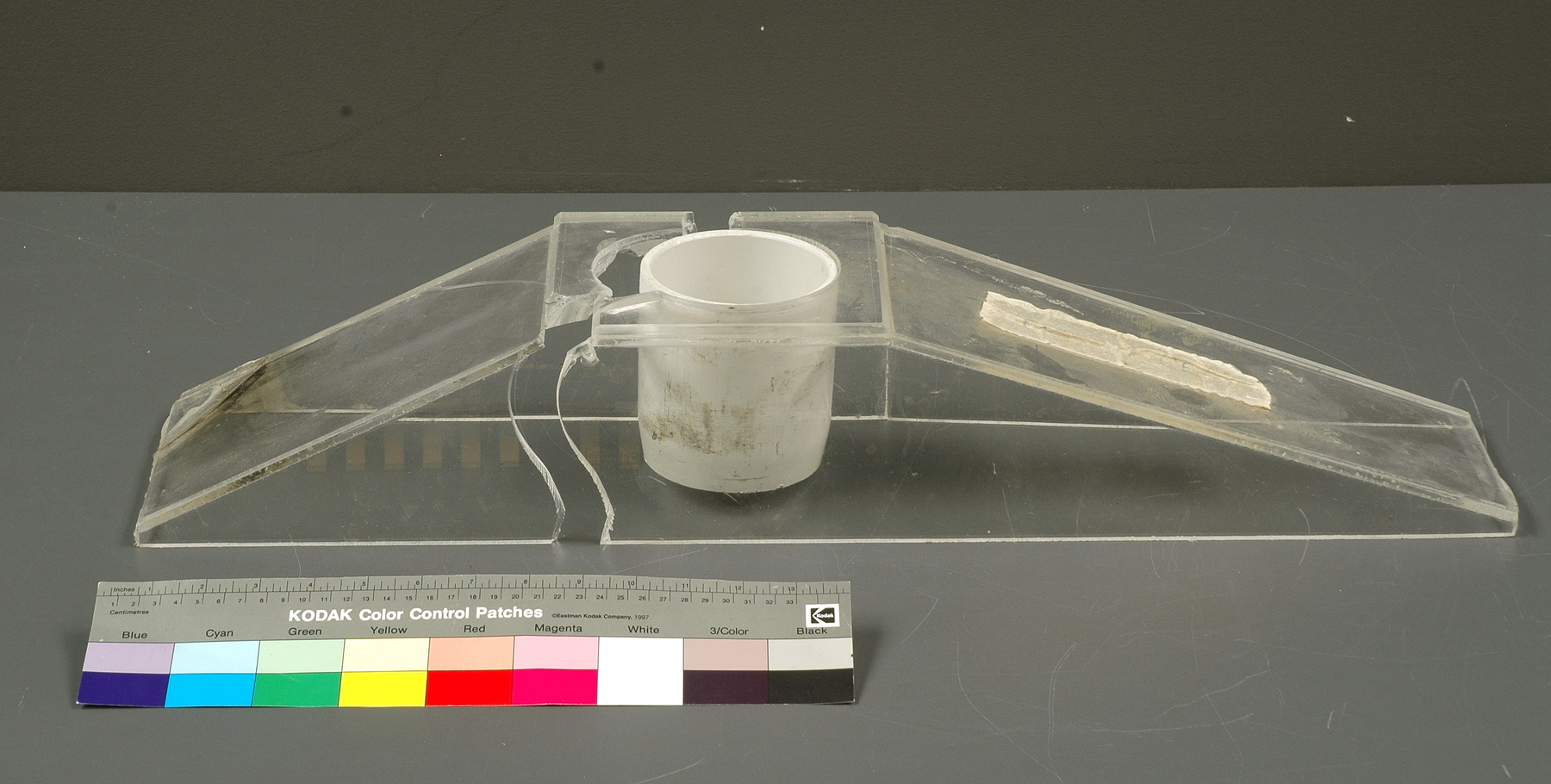
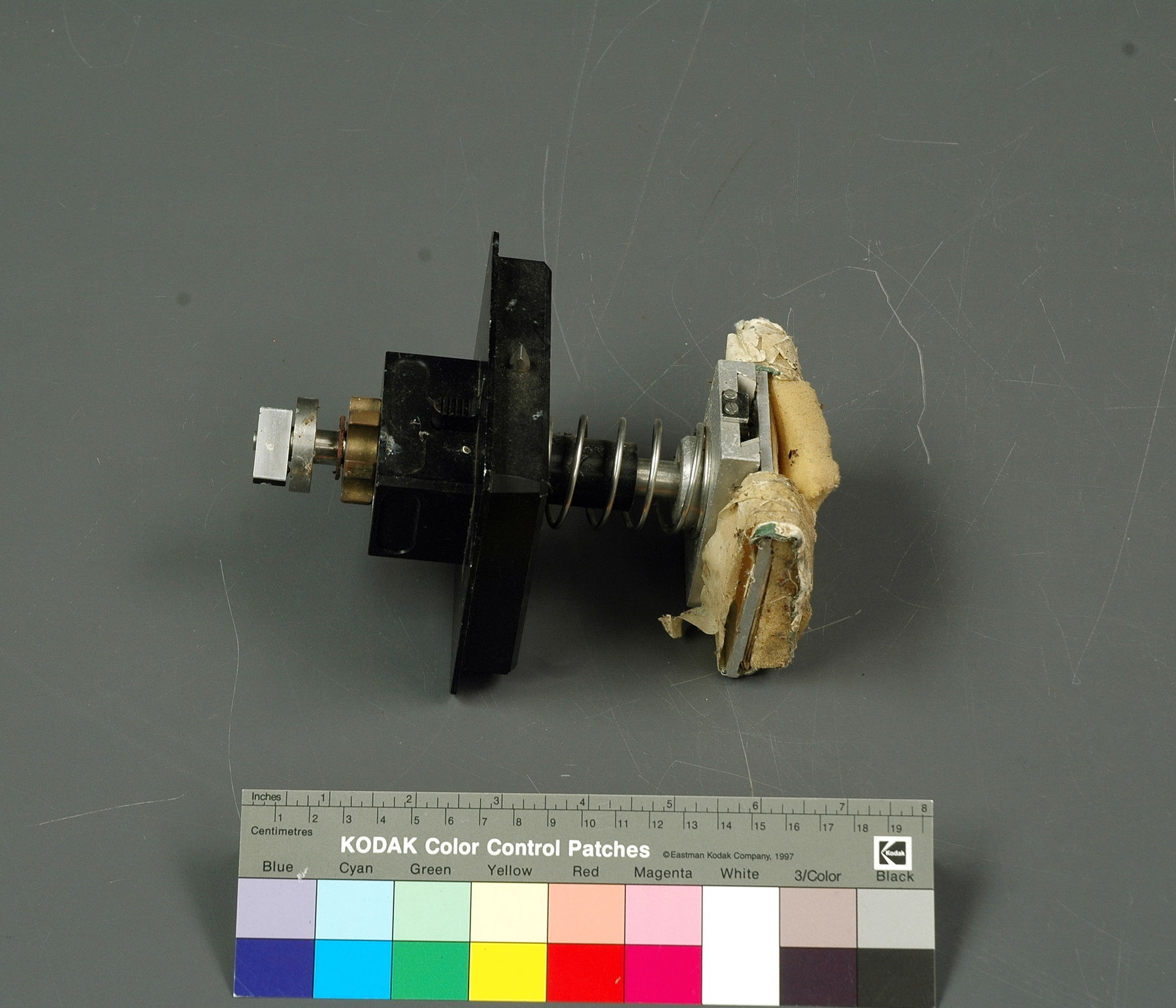
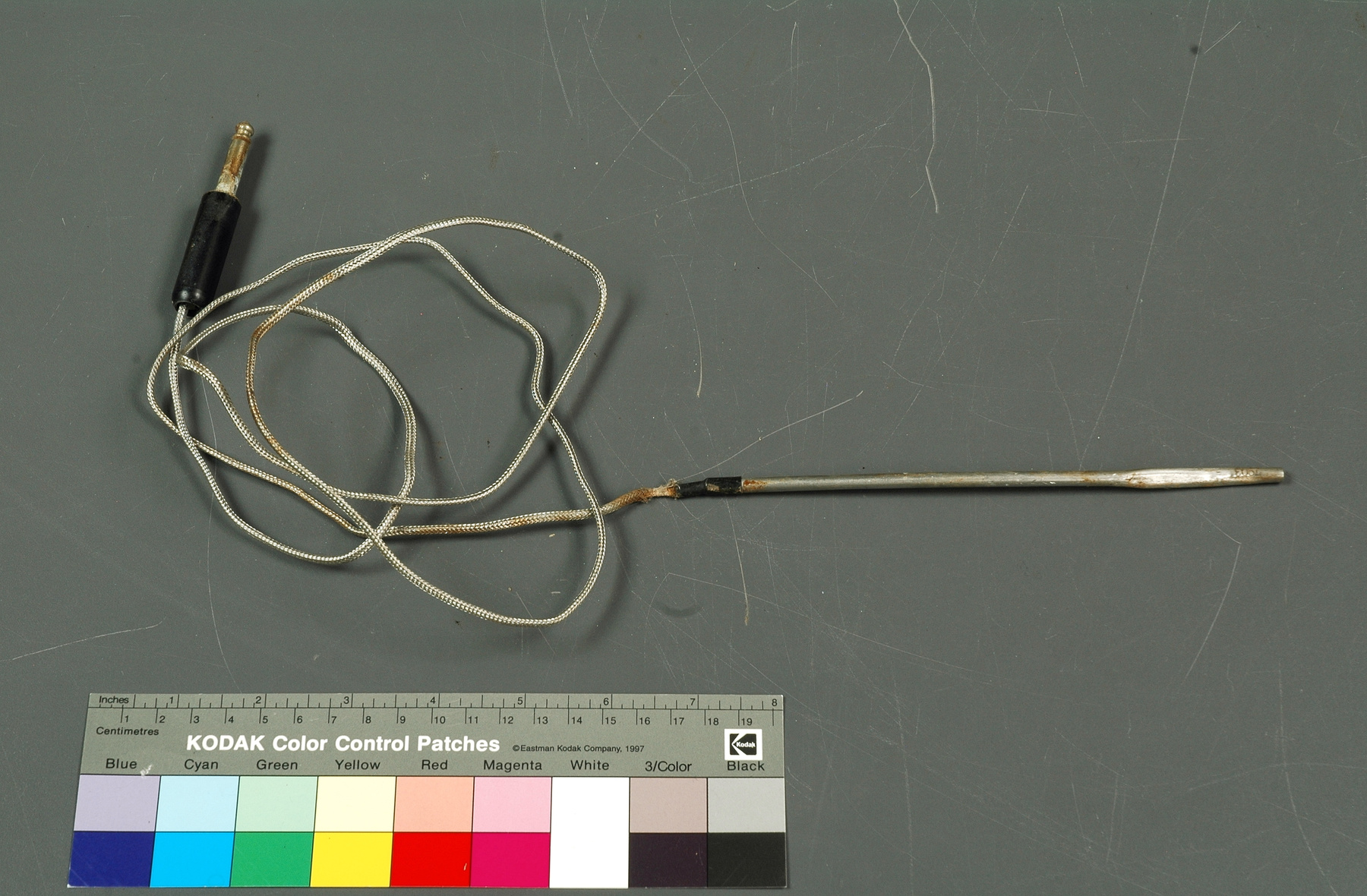
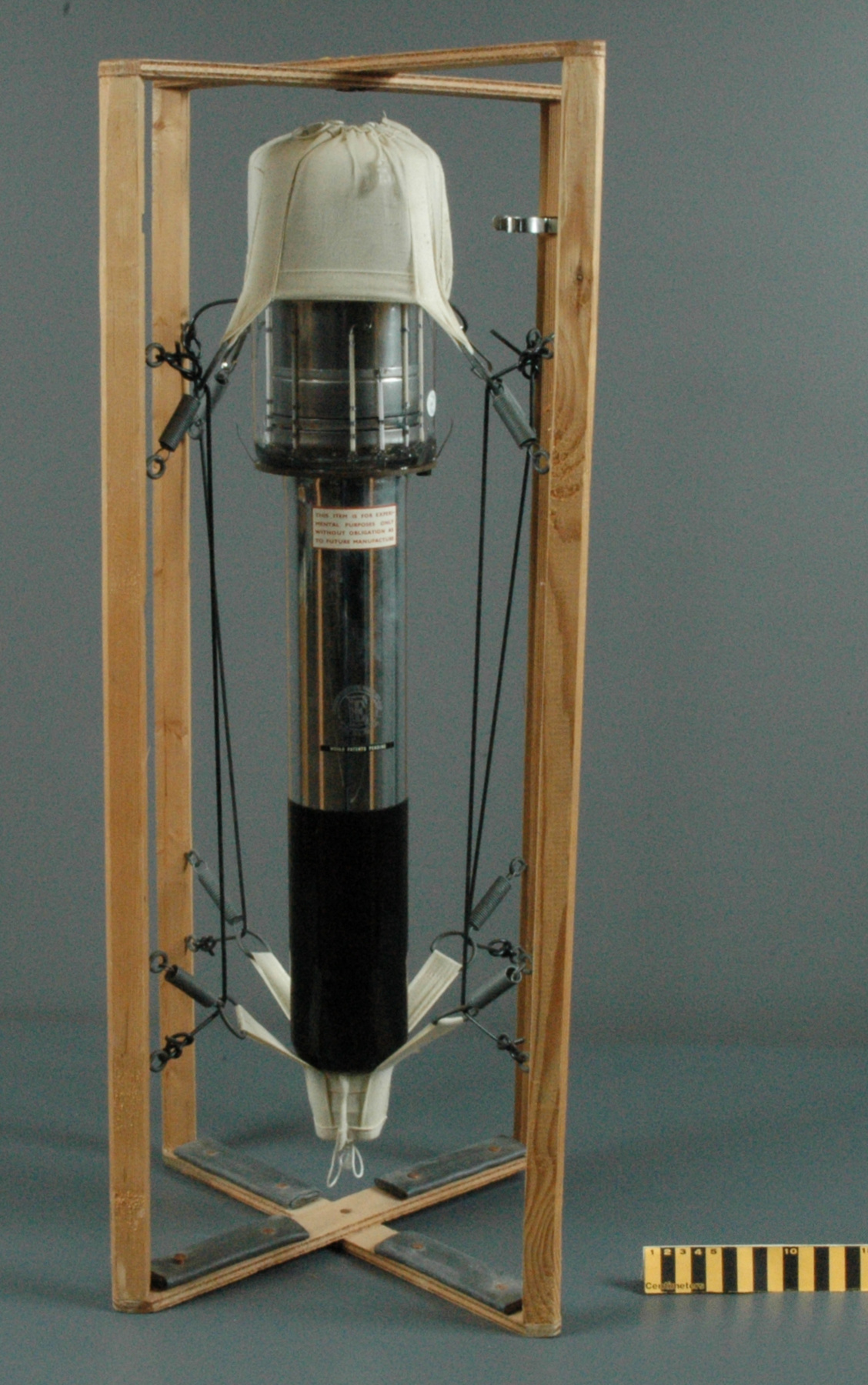
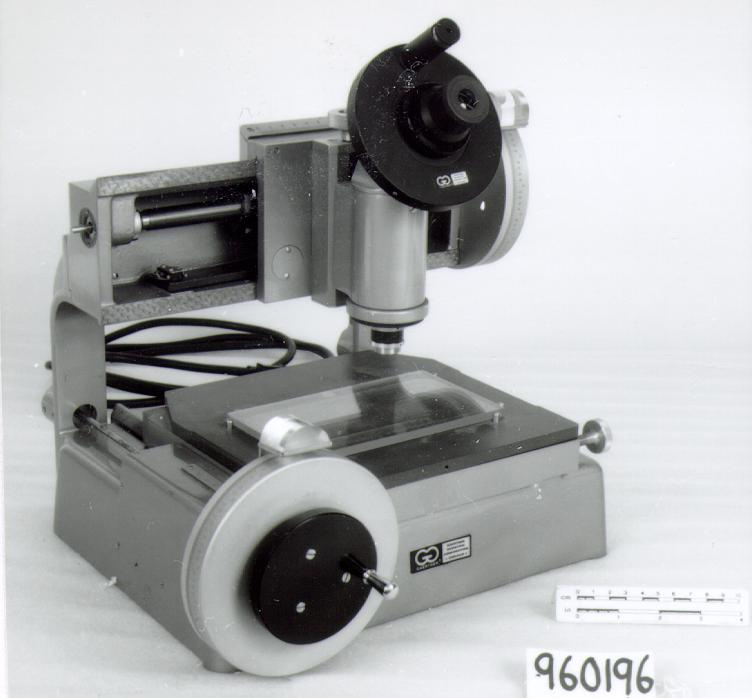
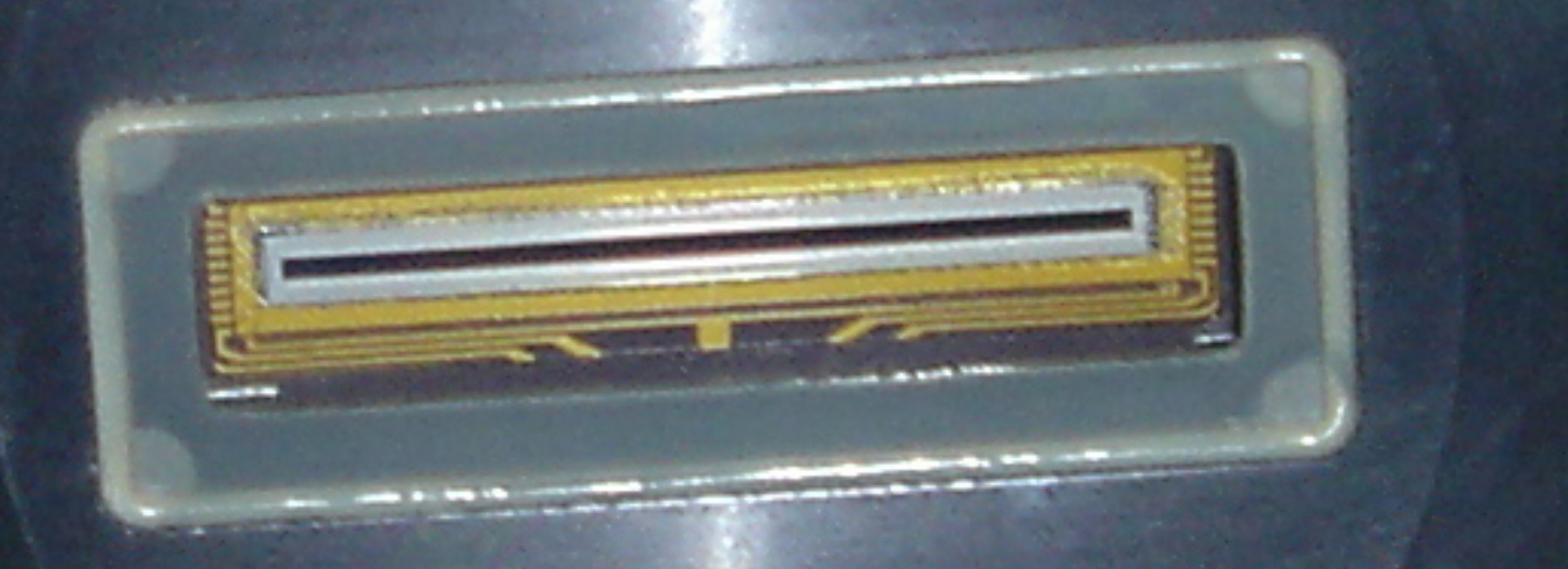
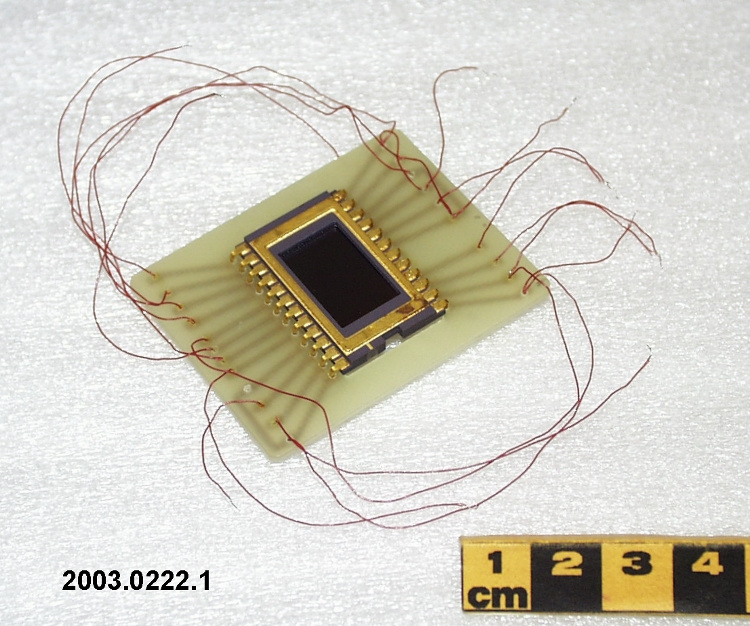
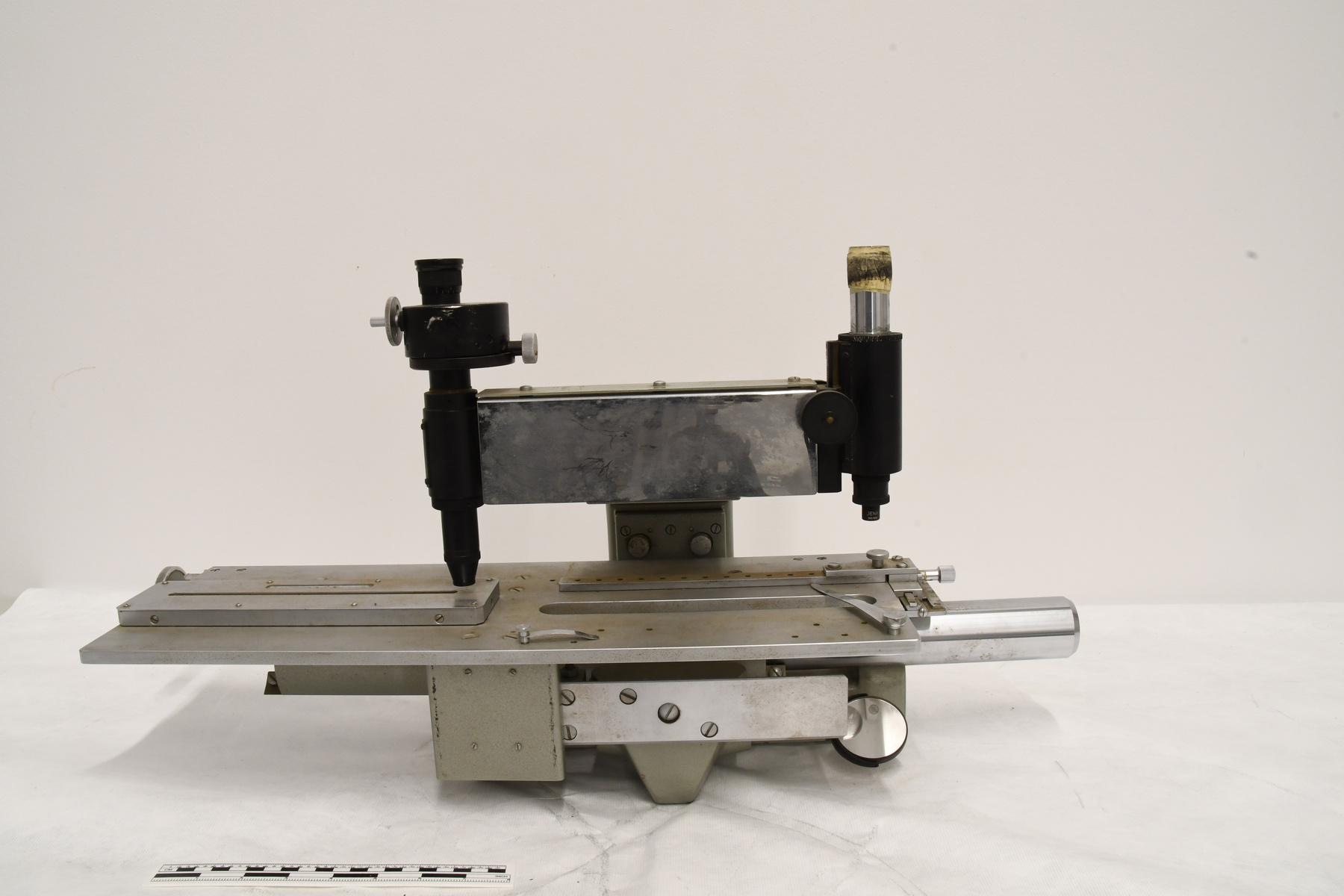
A photodiode, part of an experimental system used to record images of astronomical phenomena in order to measure stellar and galactic spectra. - Technical
-
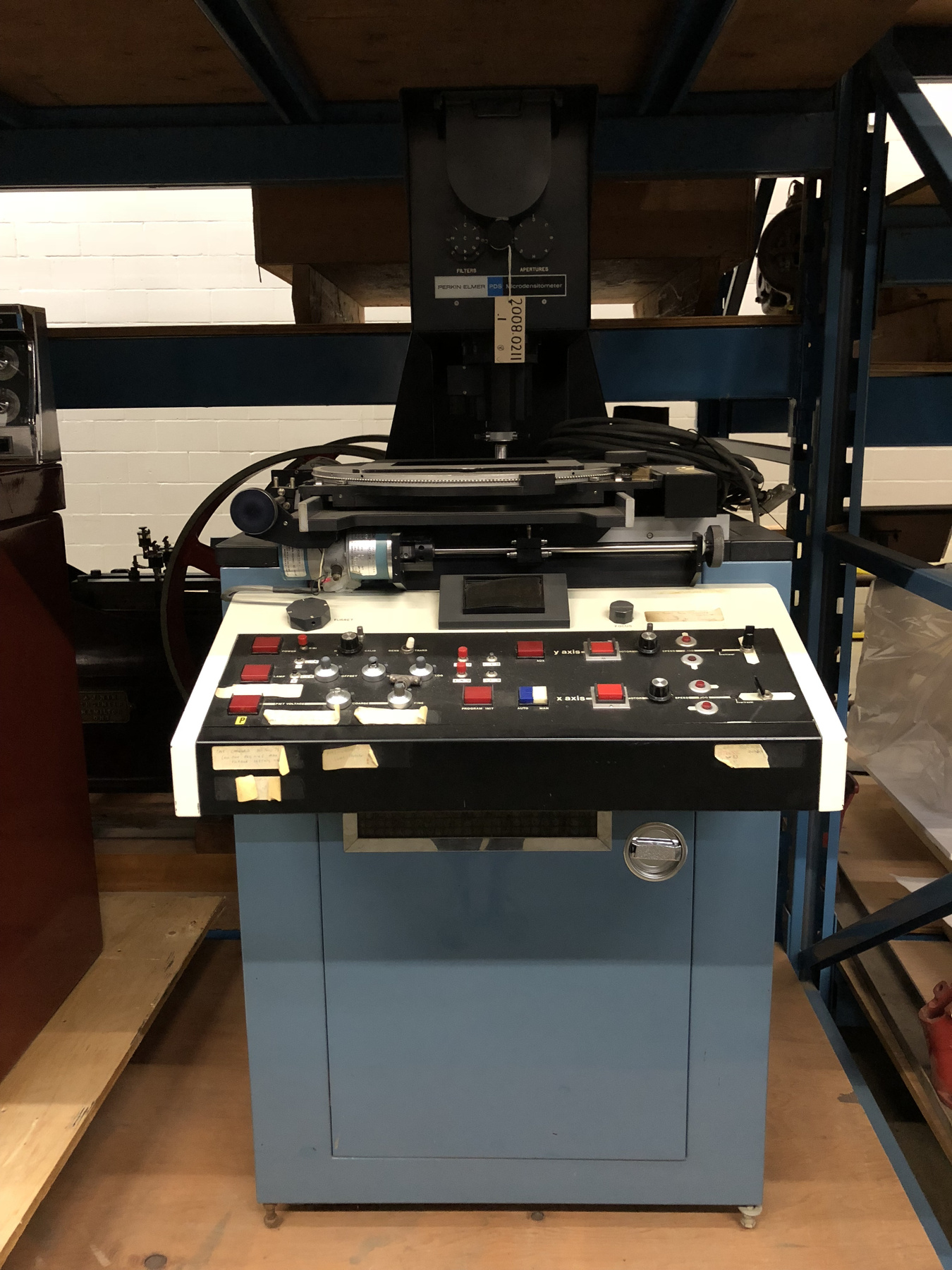
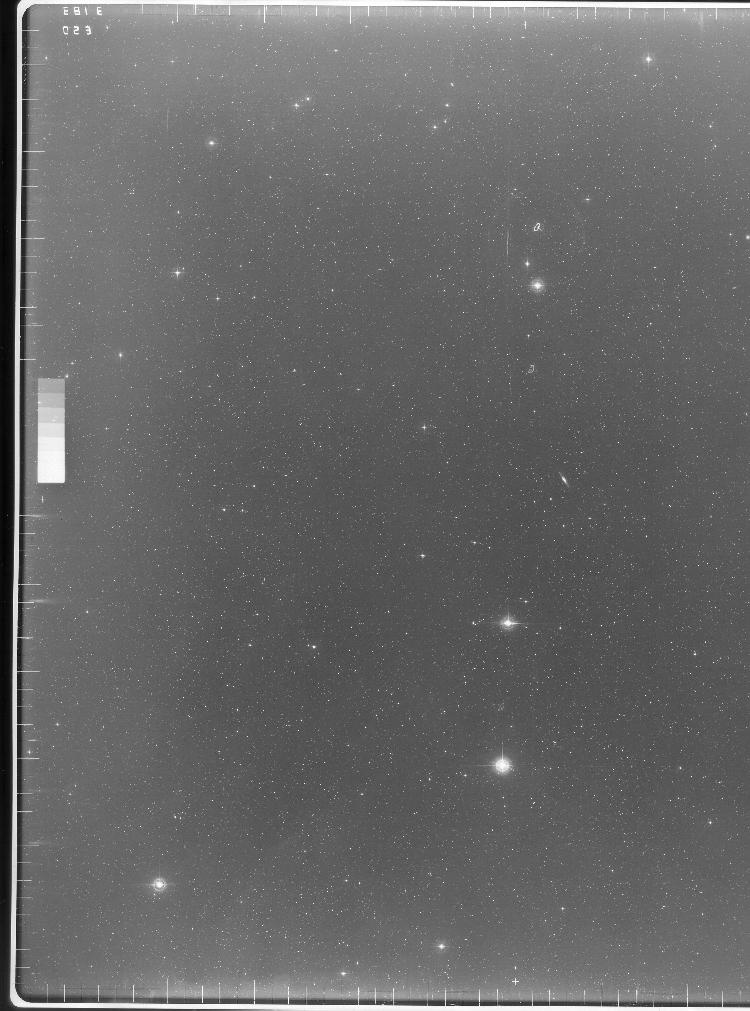
This device represents a major step from traditional photography based astronomical research and the associated equipment (e.g. microdensitometer (1998.0275), Cuffy Iris photometer) towards CCD based astronomical detectors. Its use enabled a large improvement in detector sensitivity and precision and made possible detection of rapid changes in astronomical spectra. The reticon was used with a spectrograph to determine the velocity shifts of spectral lines in stars and was a much more rapid method and with higher resolution. Typical best radial velocity measurements at this time (ca. 1970) were about 1 km/s but with the reticon, Dr. Walker and his collaborators achieved measurements of the order of 100 m/s. This technology with ever more improved detectors in the mid-1990s allowed astronomers to detect the first extra-solar system planet. By 2005, almost 200 have been discovered. - Area Notes
-
Unknown
Details
- Markings
- none
- Missing
- unknown
- Finish
- dewar: brushed metal
- Decoration
- N/A
CITE THIS OBJECT
If you choose to share our information about this collection object, please cite:
EG & G Inc., Diode, circa 1975, Artifact no. 2005.0039, Ingenium – Canada’s Museums of Science and Innovation, http://collections.ingeniumcanada.org/en/id/2005.0039.001/
FEEDBACK
Submit a question or comment about this artifact.
More Like This