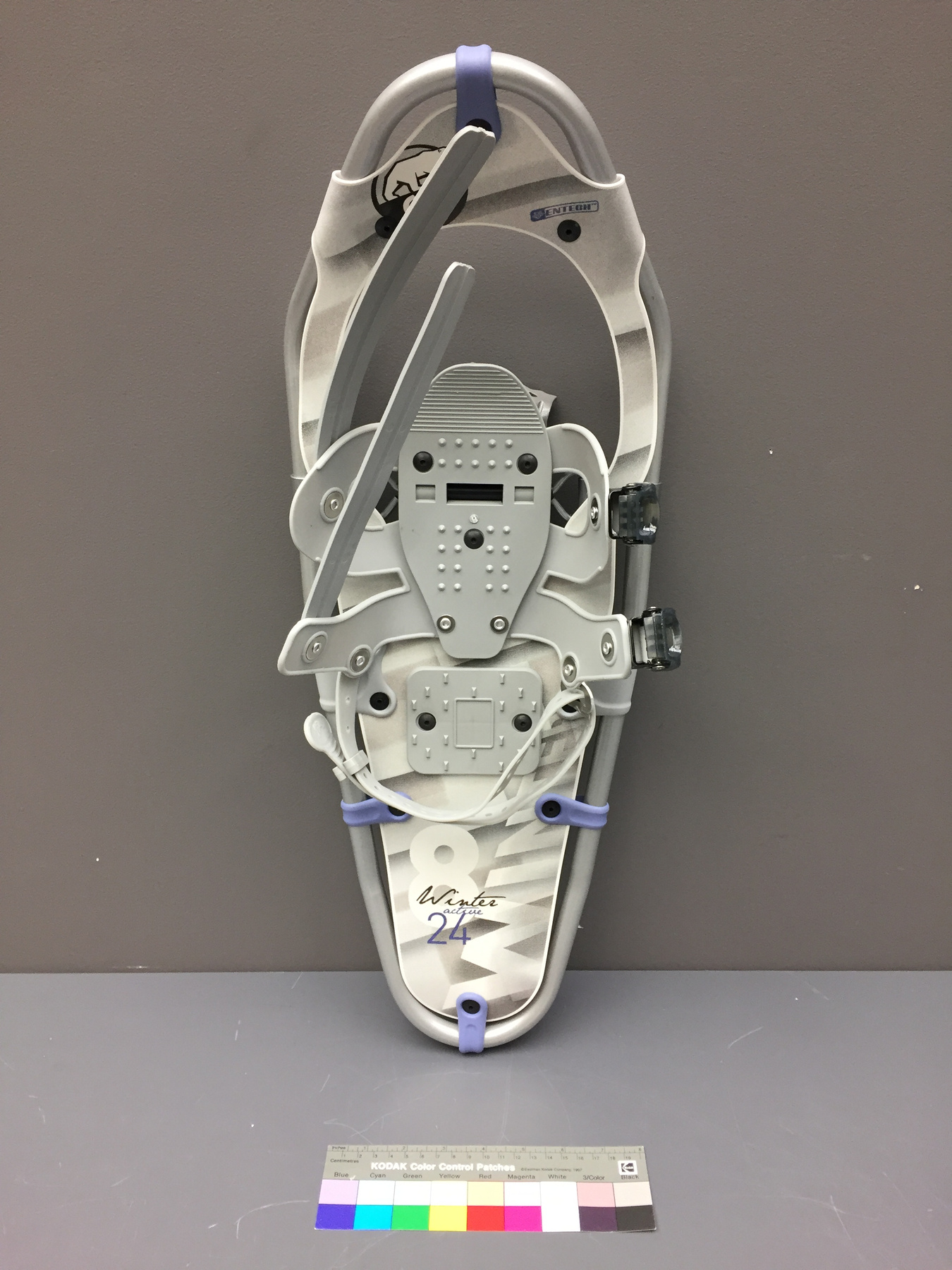
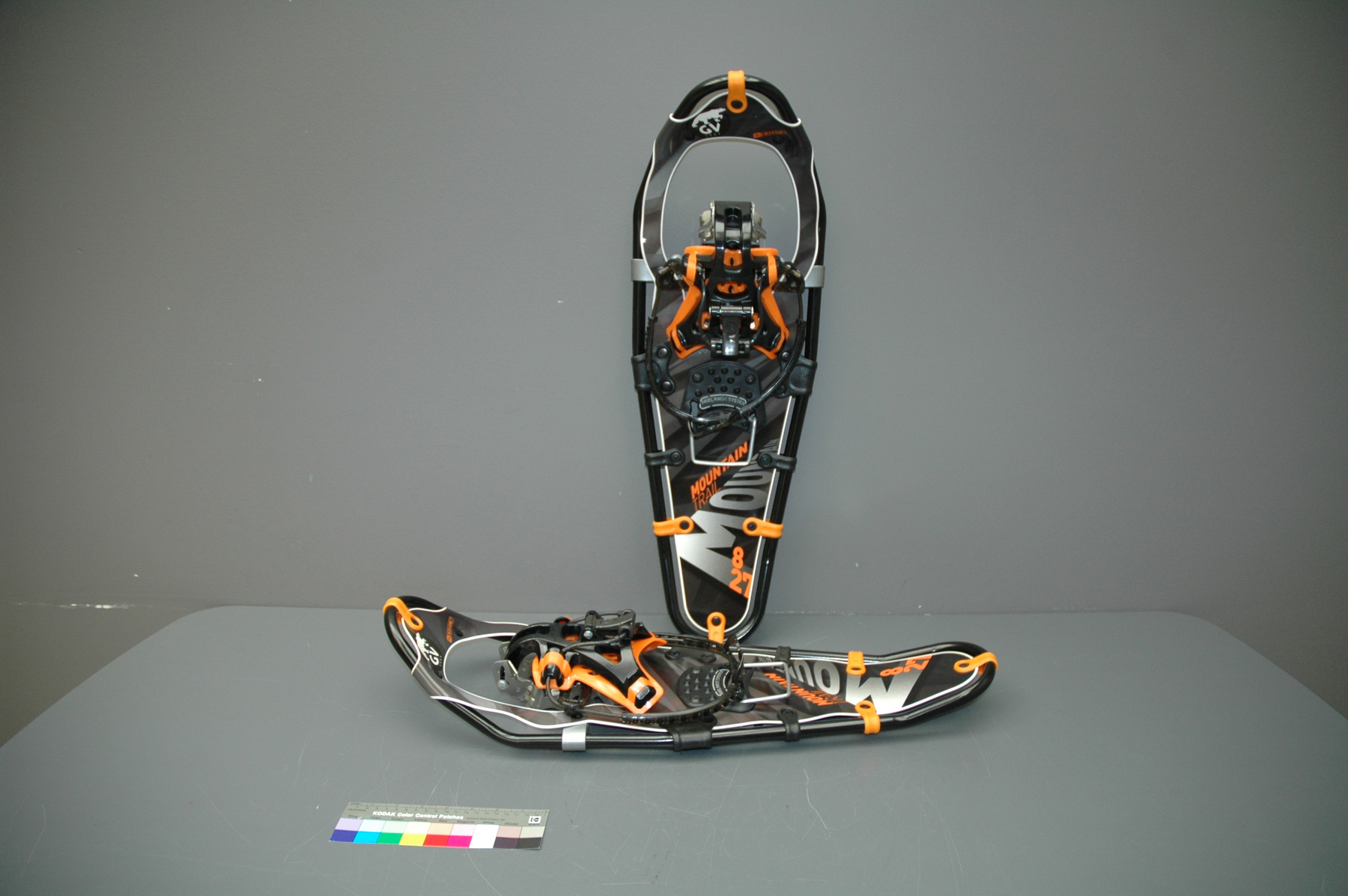
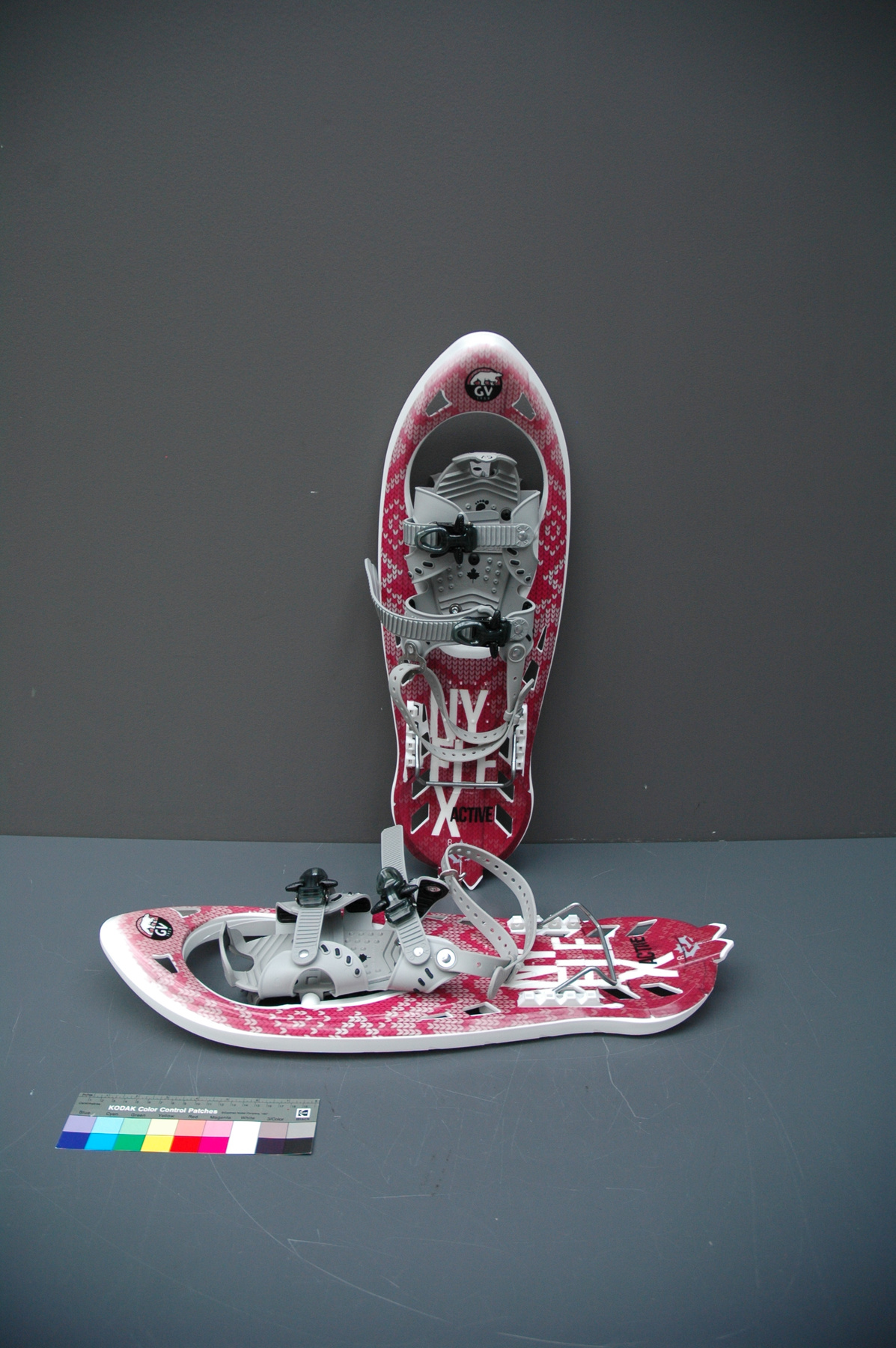
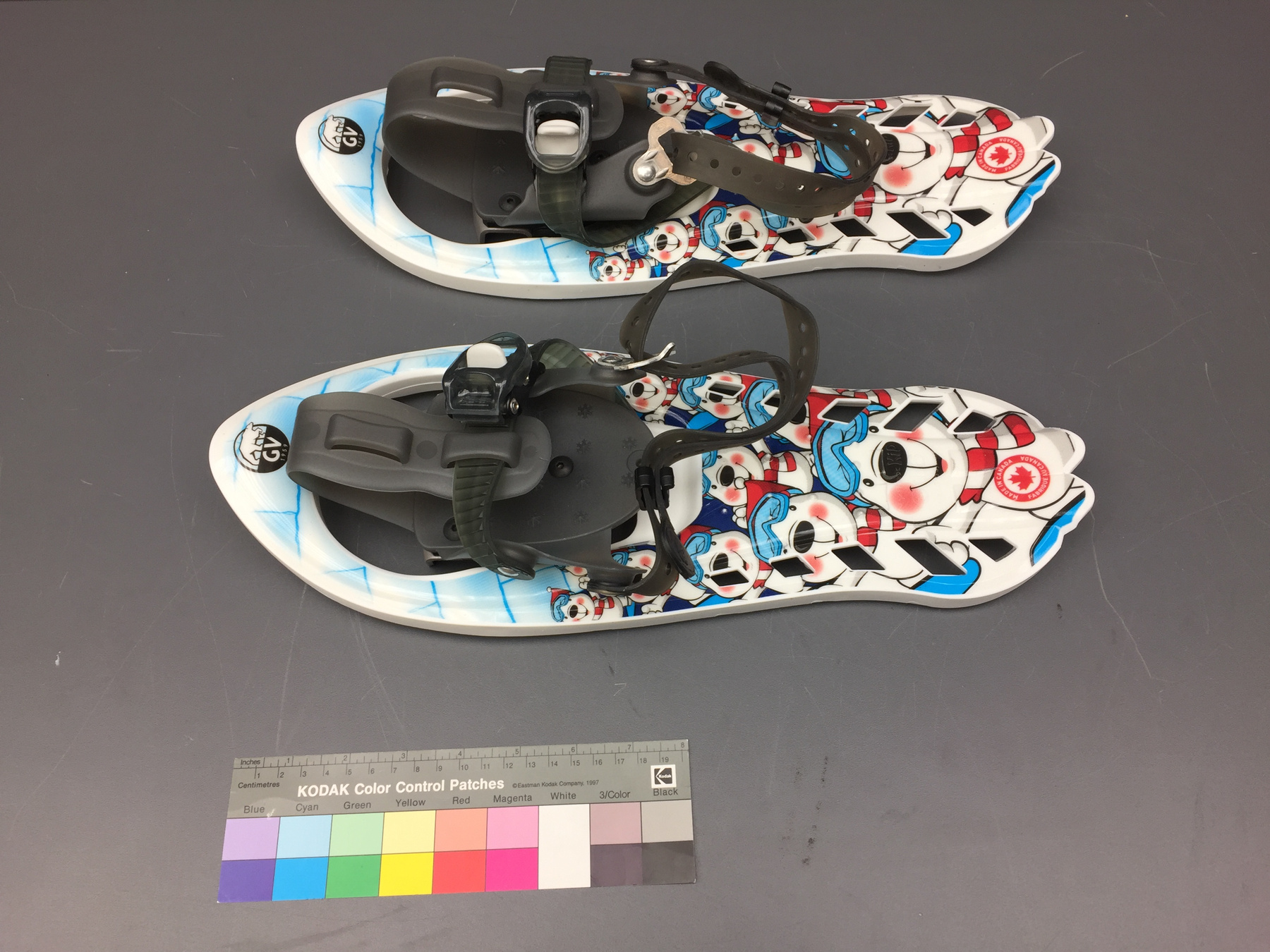
Spectrometer
Use this image
Can I reuse this image without permission? Yes
Object images on the Ingenium Collection’s portal have the following Creative Commons license:
Copyright Ingenium / CC BY-NC-ND (Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)
ATTRIBUTE THIS IMAGE
Ingenium,
2017.0147.001
Permalink:
Ingenium is releasing this image under the Creative Commons licensing framework, and encourages downloading and reuse for non-commercial purposes. Please acknowledge Ingenium and cite the artifact number.
DOWNLOAD IMAGEPURCHASE THIS IMAGE
This image is free for non-commercial use.
For commercial use, please consult our Reproduction Fees and contact us to purchase the image.
- OBJECT TYPE
- N/A
- DATE
- 1990
- ARTIFACT NUMBER
- 2017.0147.001
- MANUFACTURER
- University of Manitoba
- MODEL
- Time Of Flight 2
- LOCATION
- Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada
More Information
General Information
- Serial #
- N/A
- Part Number
- 1
- Total Parts
- 3
- AKA
- N/A
- Patents
- N/A
- General Description
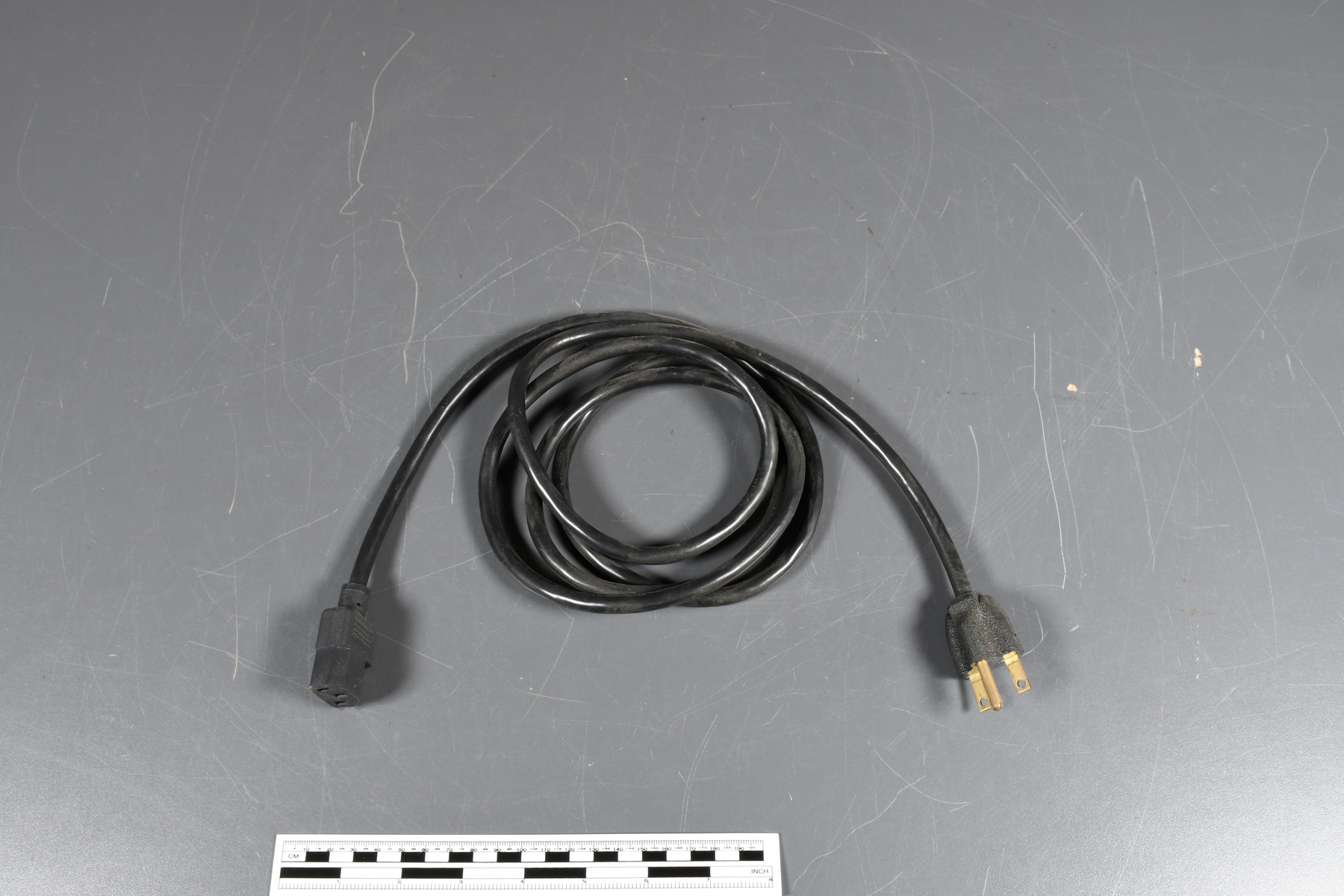
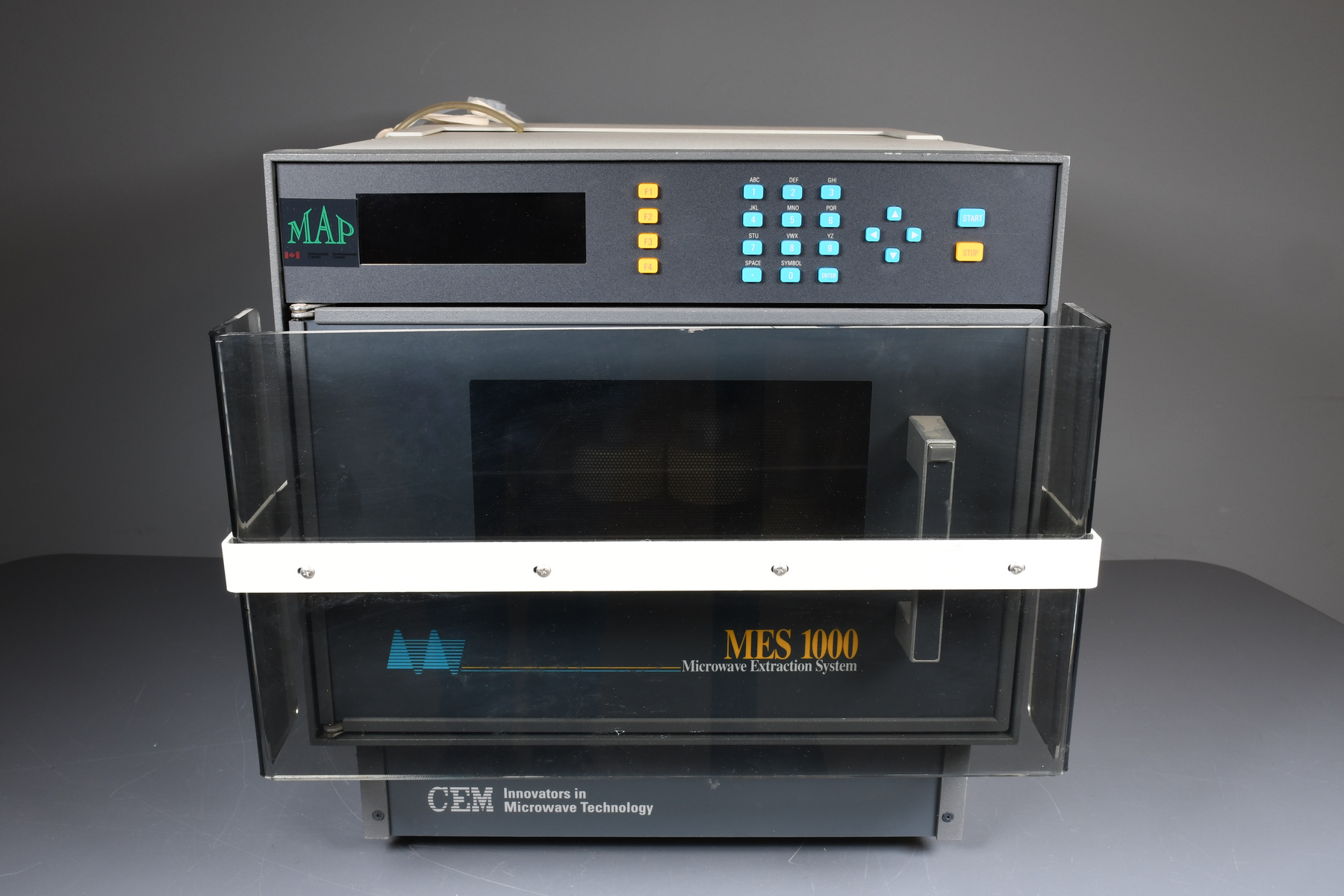
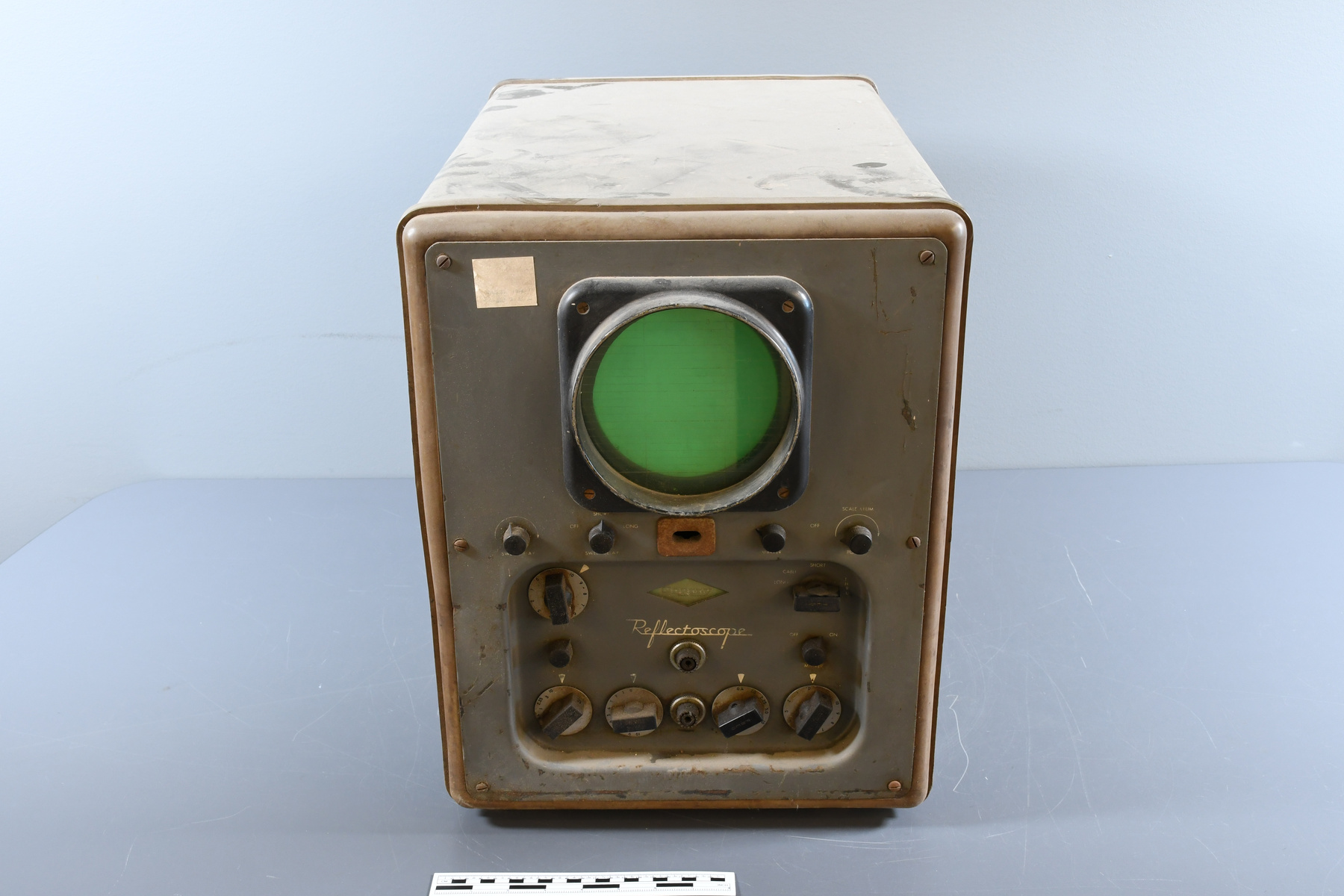
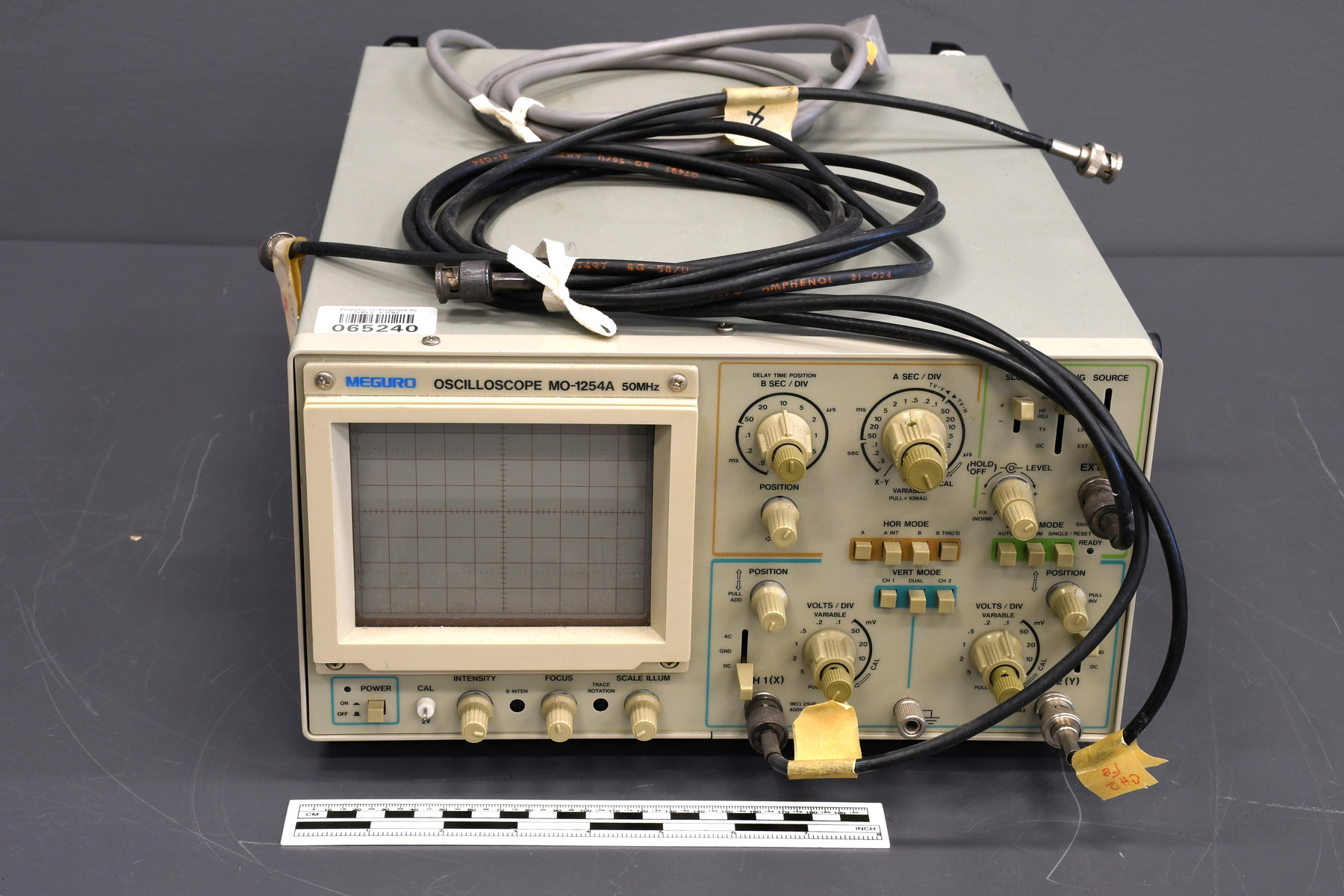
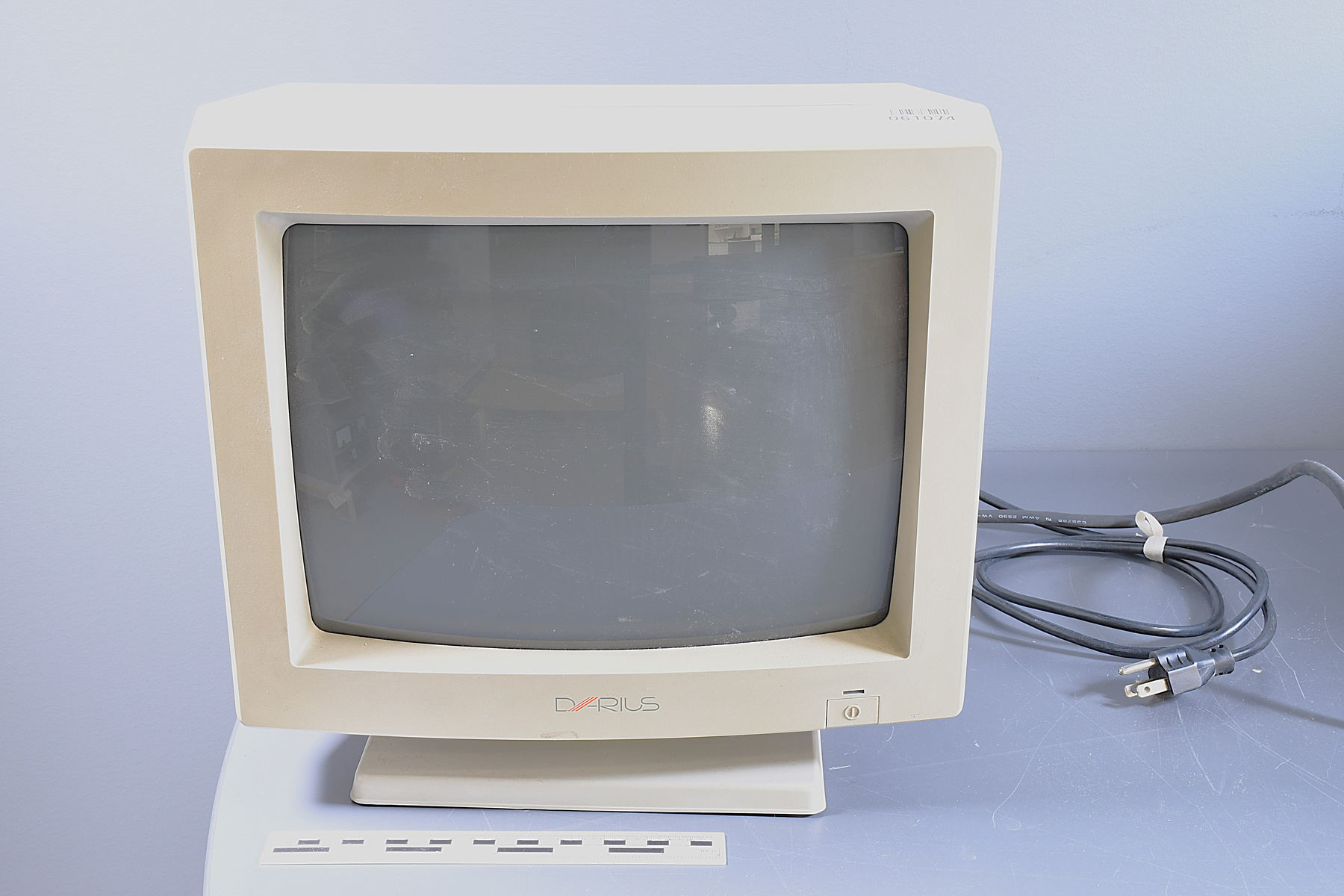
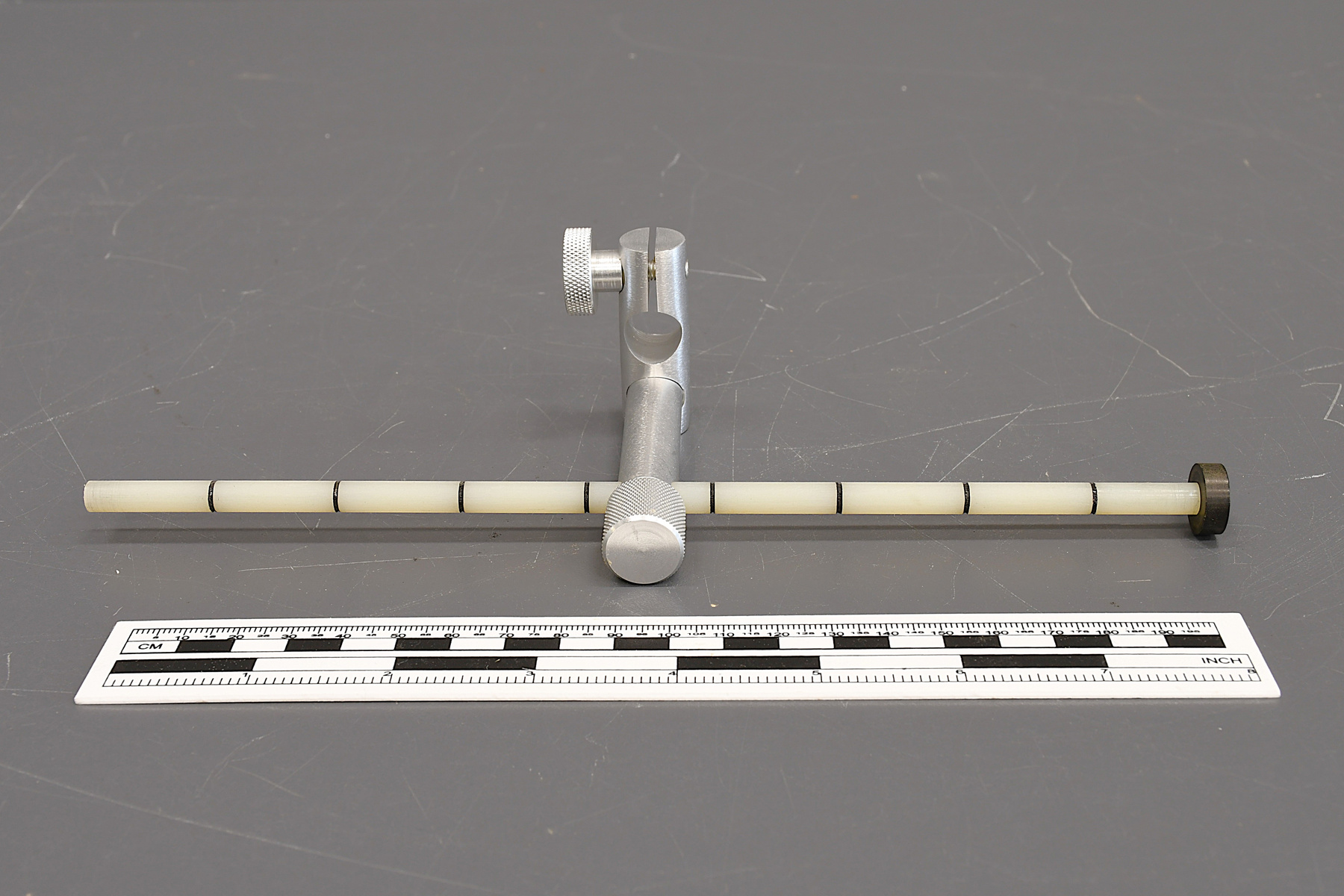
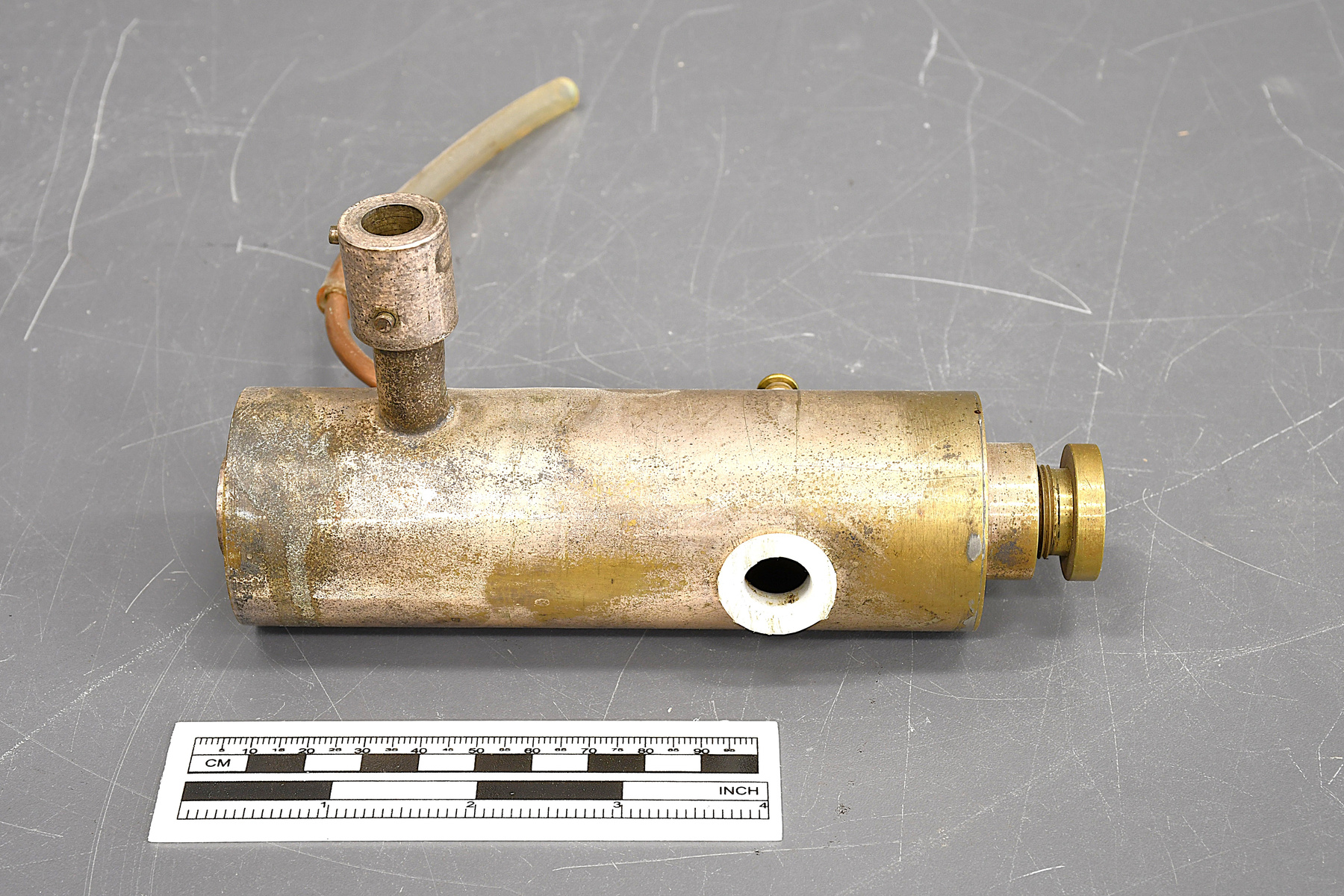
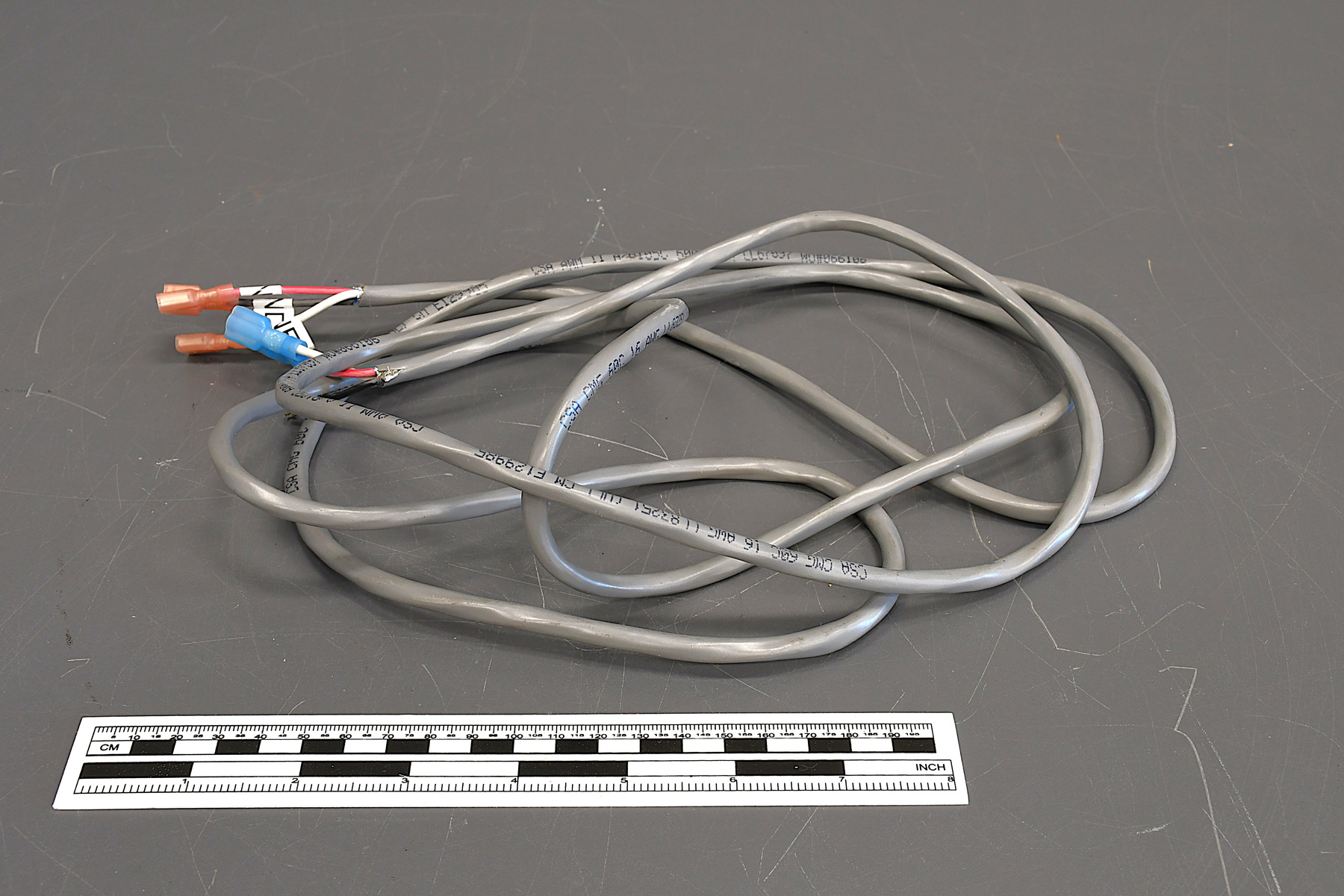
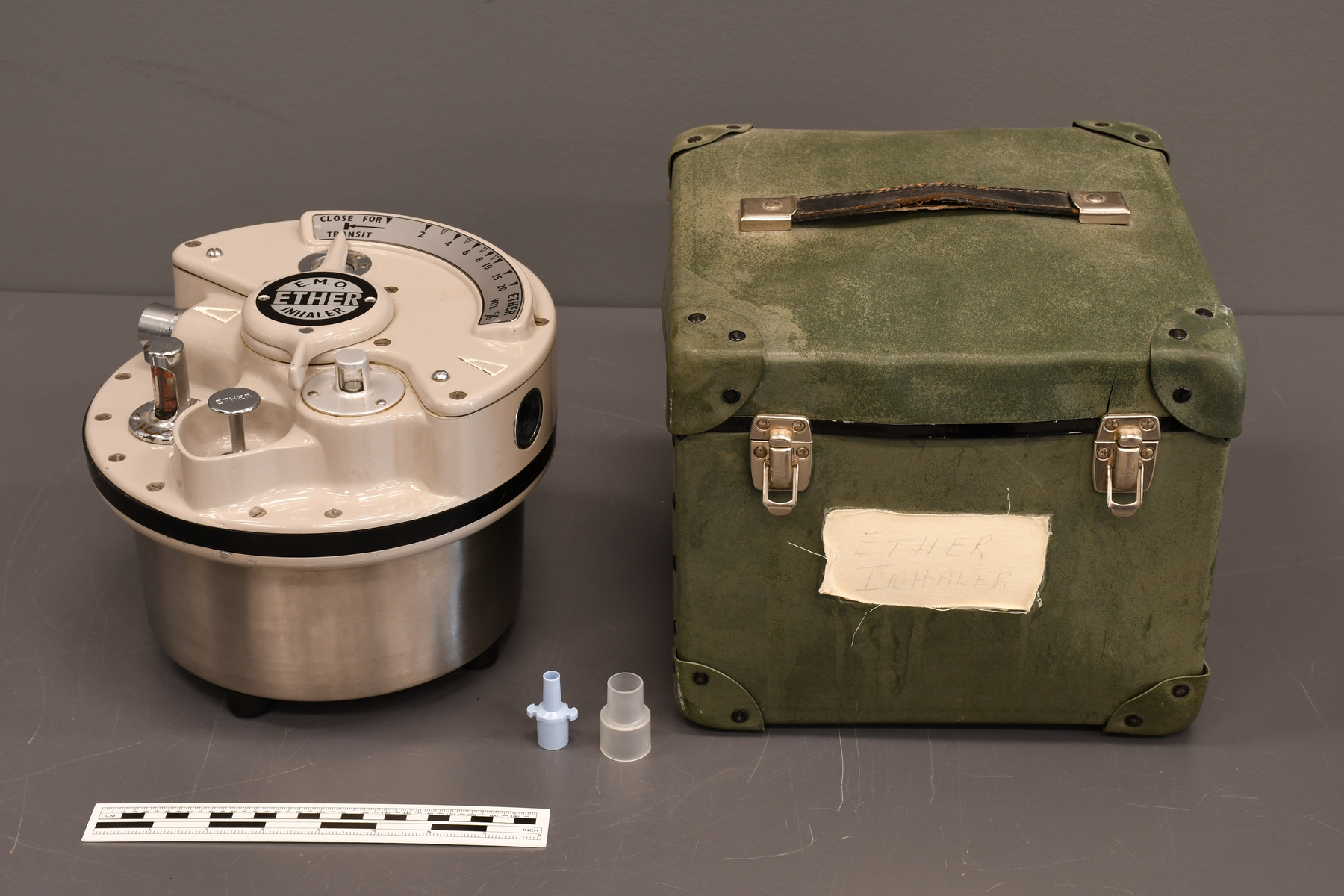
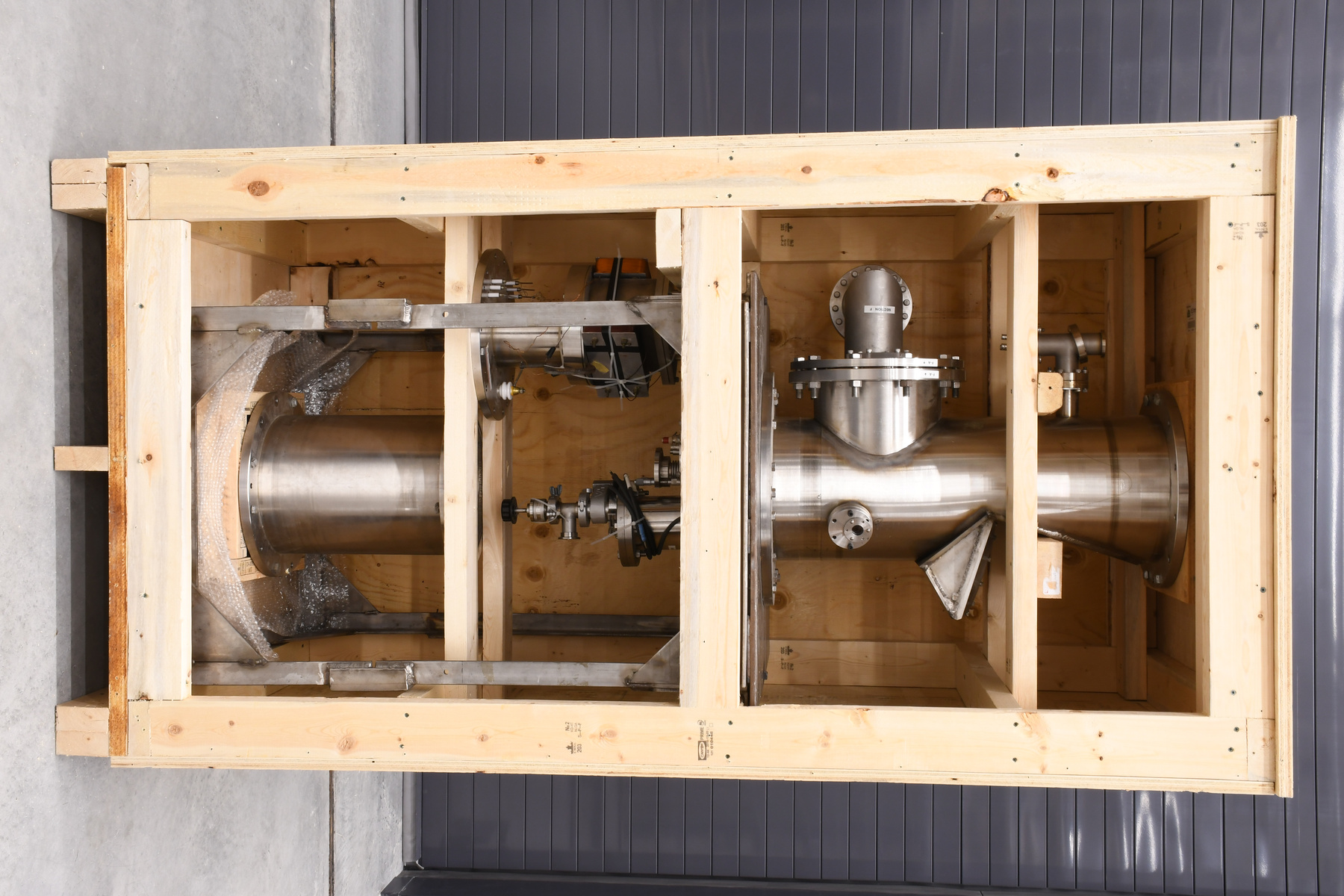
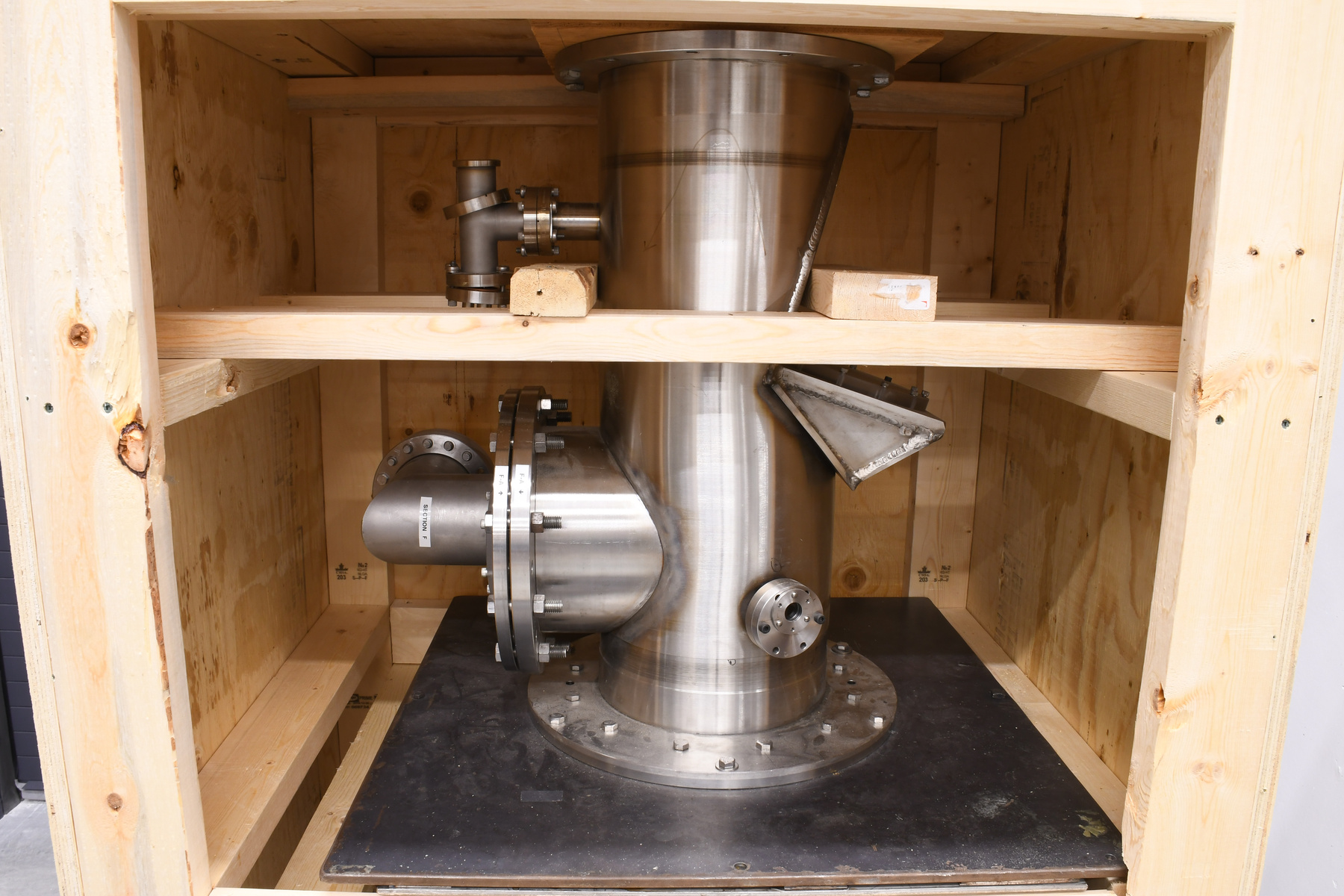
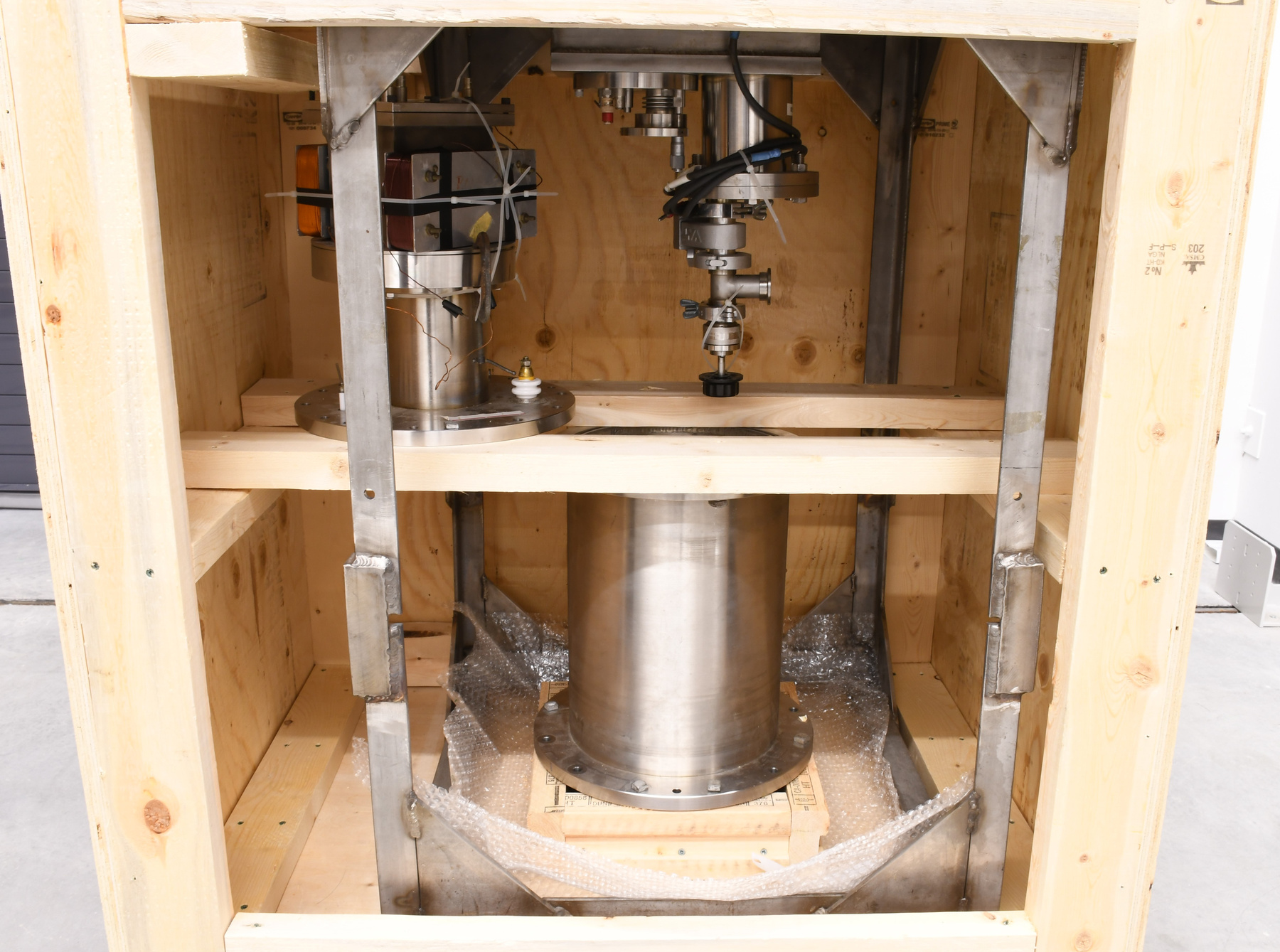
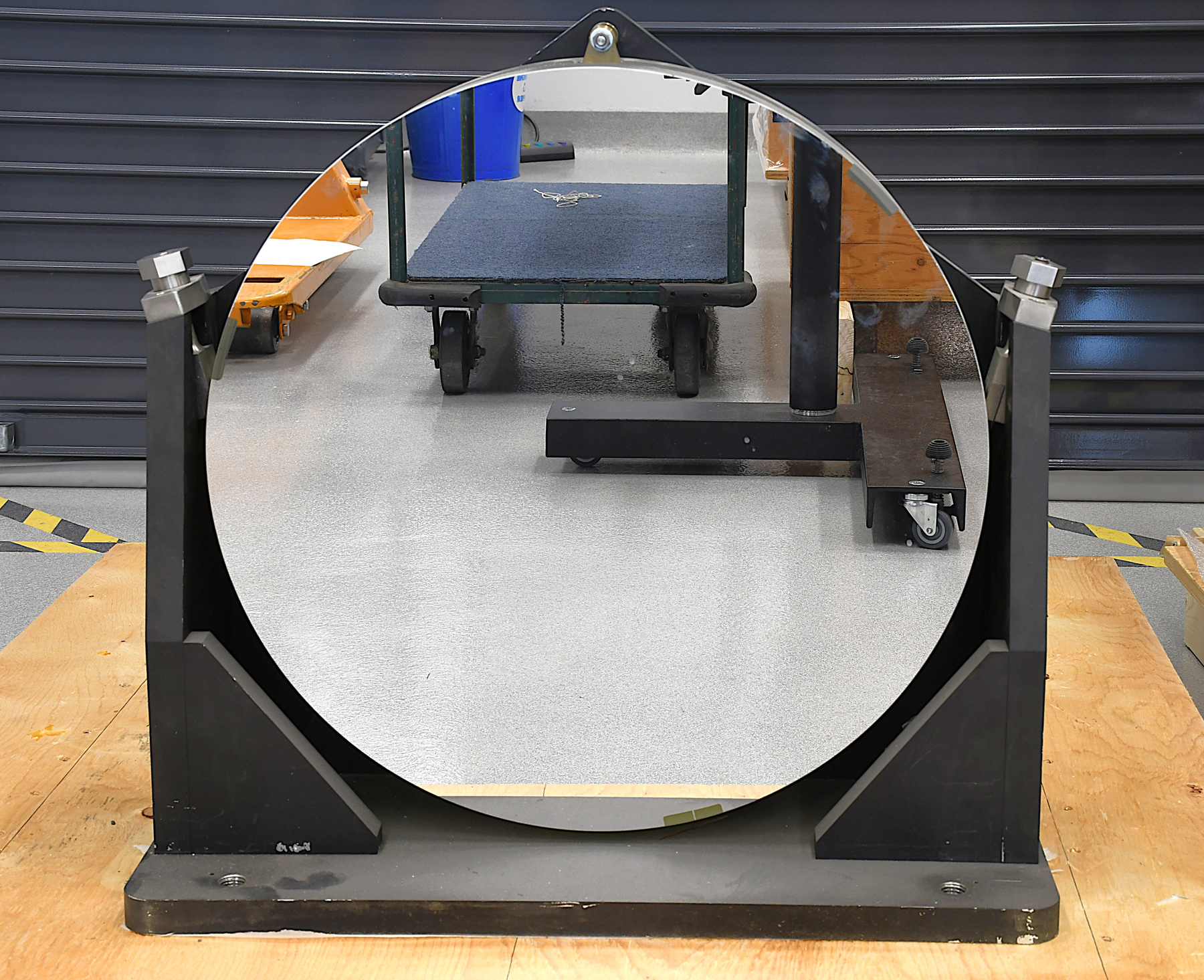
- Time Of Flight 2 mass ppectrometer designed and built entirely at the University of Manitoba. Spectromètre de masse Time Of Flight 2 conçue et construit entièrement à l'Université du Manitoba.
Dimensions
Note: These reflect the general size for storage and are not necessarily representative of the object's true dimensions.
- Length
- 80.0 cm
- Width
- 20.3 cm
- Height
- 185.4 cm
- Thickness
- N/A
- Weight
- N/A
- Diameter
- N/A
- Volume
- N/A
Lexicon
- Group
- Medical Technology
- Category
- N/A
- Sub-Category
- N/A
Manufacturer
- AKA
- University
- Country
- Canada
- State/Province
- Manitoba
- City
- Winnipeg
Context
- Country
- Unknown
- State/Province
- Unknown
- Period
- Unknown
- Canada
-
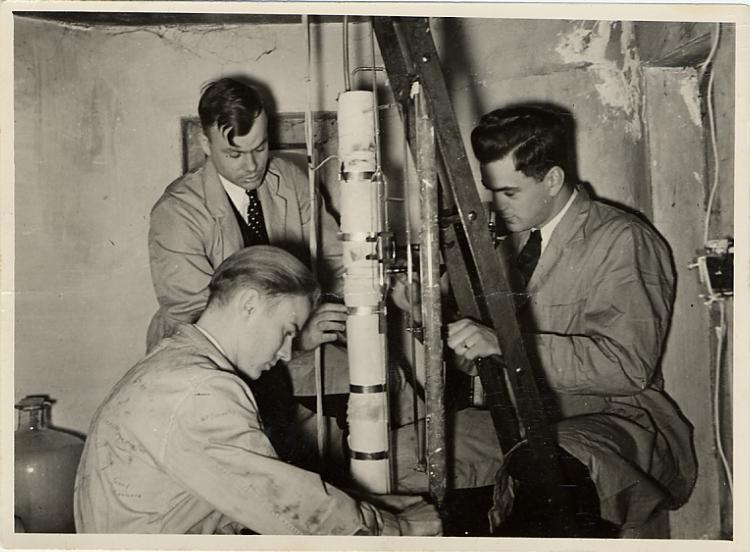
It has been over one hundred years since British scientists developed methods to deflect ions (charged particles) of different mass in order to study the make-up of materials. Scientists at U of Manitoba have since become masters of these effects; they have made significant contributions in two areas of mass spectrometry: the determination of fundamental mass units, and the analysis of large biological molecules. Researchers, engineers and instrument makers around the world use U of M findings and technologies in physics, chemistry, health sciences and industry. Why Winnipeg? The " Manitoba II " is the anchor of Mass Spec studies at U of M; It is a room-sized, high-resolution mass spectrometer that has set international standards for determining atomic masses. It is a curved one-meter radius electromagnetic track followed by a large electromagnet for deflecting and detecting ions. In the late 1970s ion deflection turned into straight flight when Ken Standing and his post doc, Brian Chait, developed a way to analyse big organic molecules using Time of Flight (TOF) mass spectrometry. Werner Ens joined Standing as a Phd student just as this instrument began to work. Ens joined the faculty in 1987, and in 2010, Standing and Ens won the Manning Innovation award for their achievements. Between those years there were three significant instruments built at the U of M - The TOF1 (c. 1979), TOF2 (c.1990), and TOF4 (c.1994). The major players in these developments have suggested that the corporation acquire the TOF2 instrument because it represented a major breakthrough in the field at the time, and it was entirely built at U of M. Il y a au-delà de cent ans depuis que les scientifiques britanniques ont développé des méthodes pour dévier des ions (particule chargée) de différentes masses pour but d’étudier la composition de matériaux. Les scientifiques à l’Université du Manitoba sont dorénavant devenus les maitres à ces effets; ils ont fait plusieurs grandes contributions dans deux secteurs de la spectrométrie en masse : la détermination de l’unité de masse fondamentale et l’analyse de grandes molécules biologique. Des chercheurs, des ingénieurs et des constructeurs d’instruments autour du monde utilisent les découvertes technologiques de l’Université du Manitoba en physique, chimie, science de la santé et l’industrie. Pourquoi Winnipeg? Le « Manitoba II » est le point d’emphase des études de la spectrométrie en masse à l’Université du Manitoba. C’est un spectromètre en masse à haute résolution à taille de pièce qui a mis en place les standards internationaux pour l’étude des masses atomiques. Le Manitoba II est un rail électromagnétique à un radius d’un mètre qui est suivi avec un grand électroaimant pour dévier et détecter des ions. Vers la fin des années 1970s, la déviation des ions est devenu un vol direct lorsque Ken Standing et Brian Chait ont développé une manière d’analyser des molécules organiques en utilisant le temps de vol. Werner Ens s’est rejoint Standing en tant qu’étudiant de doctorat lorsque cet instrument était dans ses premiers stages. Warner Ens s’est rejoint à la faculté en 1987 et en 2010, Standing et Ens ont gagné le prix d’Innovation Manning pour leurs accomplissements. Entre ces années, on remarque trois instruments significatifs construits à l’Université du Manitoba – Le TOF1 (c. 1979), TOF2 (c.1990), and TOF4 (c.1994). Les grands joueurs dans ces développements et ont suggéré que la Société devrait acquérir l’instrument TOF2 étant donné qu’il représente une percée importante dans ce champ, et qu’il a été bâti entièrement à l’Université du Manitoba. - Function
-
Scientific instrument designed to analyze (or separate in order to "read" ) the materials and bio-materials by using the different mass of their consituents. Instrument scientifique utilisé pour analyser (ou séparer pour "lire") les matériaux et les biomatériaux en utilisant les différentes masses de leurs constituants. - Technical
-
The TOF 2 represents key developments that led to the commercialization and success of Mass Spectrometry at the University of Manitoba. It has orthogonal injection, MALDI techniques and collisional cooling. It was designed and built entirely at the University of Manitoba. The following is an excerpt from the Manning Award citation: " The problem was, when it came to analyzing relatively large biomolecules, such as proteins, early TOF techniques did not work very well. (...) Even with electrospray or MALDI, accurate TOF measurements were hard to get because it was like a race in which some runners were thrown out of the starting gate and others started flat on their backs. To level the playing field, Ken Standing and Werner Ens decided to separate the ion source from the TOF analyzer and introduce two key innovations: a quadrupole ion guide used to cool the ions, and orthogonal injection, to introduce the ions at a right angle to the "racetrack". With these innovations, the ions would all start the race with their feet on the starting line. " Le TOF 2 représente un développement clé qui a mené à la commercialisation et le succès de la spectrométrie de masse à l'Université du Manitoba. Il y a une injection orthogonale, les techniques de désorption-ionisation laser assistée par matrice et le refroidissement collisionnel. Le TOF 2 a été conçu et construit entièrement à l'Université du Manitoba. La prochaine citation est un extrait du Prix Manning: " Le problème était, en ce qui concerne l'analyse de large biomolécule, comme des protéines, les premières techniques de temps de vol ne fonctionnaient pas très bien. Même avec l'électronébulisation où les techniques de désorption-ionisation laser assistée par matrice, les mesures précises du temps de vol étaient difficiles à lire tandis que c'est comme une course ou certain coureurs commencent rapidement au début de la course et les autres trébuchent et tombent dès du début. Pour améliorer l'analyse, Ken Standing et Werner Ens ont décidé de séparer la source d'ions de l'analyseur du temps de vol et introduire deux innovations clés; un guide quadrupôle d'ions utilisé pour réfrigérer les ions, et l'injection orthogonale, pour introduire les ions à un angle droit à la "course". Avec ces innovations, les ions vont commencer la course en même temps. " - Area Notes
-
Unknown
Details
- Markings
- N/A
- Missing
- Appears complete.
- Finish
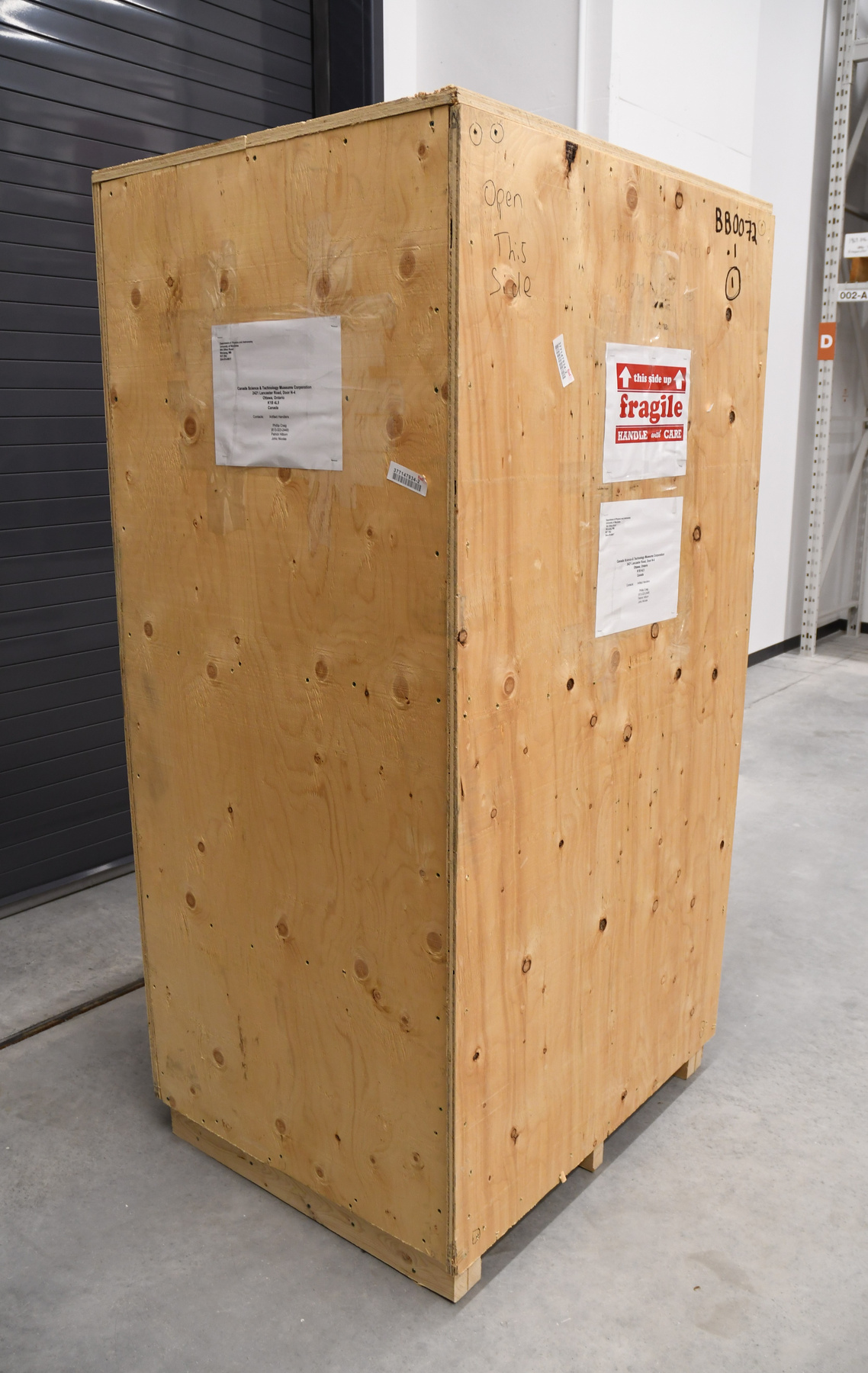
- Mass spectrometer made primarily from silver coloured steel and alloys. The spectrometer also has glass, plastics and rubber components and details. The spectrometer is currently supported and stabilized in its wooden shipping crate. Spectromètre de masse fabriqué principalement par de l'acier en couleur argentée et de l'alliage. Le spectromètre a aussi des composantes et des détails en verre, plastique et caoutchouc. Le spectromètre est présentement appuyé et stabilisé dans sa caisse d'expédition de bois.
- Decoration
- N/A
CITE THIS OBJECT
If you choose to share our information about this collection object, please cite:
University of Manitoba, Spectrometer, circa 1990, Artifact no. 2017.0147, Ingenium – Canada’s Museums of Science and Innovation, http://collections.ingeniumcanada.org/en/id/2017.0147.001/
FEEDBACK
Submit a question or comment about this artifact.
More Like This